Figure 3.
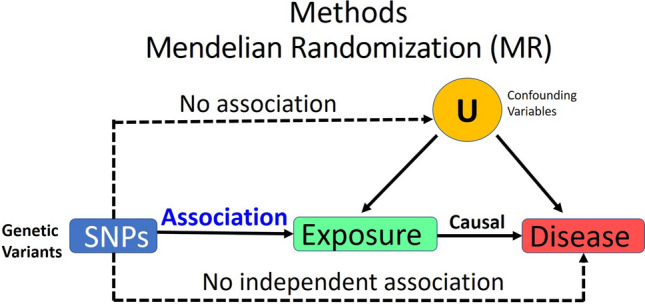
Mendelian Randomization unbiased causal associations and assumptions. Mendelian Randomization (MR) is an application of the instrumental variable using genetic variants Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS), and Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs). MR requires several stringent assumptions to be fulfilled. First, no confounders are associated with the genetic instrument; and second, the genetic proxy of exposure (SNP) should not be independently associated with the disease outcome, but only mediates its effect via the relevant exposure. The SNPs used in the study had no association with the confounding variables (U) and no independent association with diabetes.
