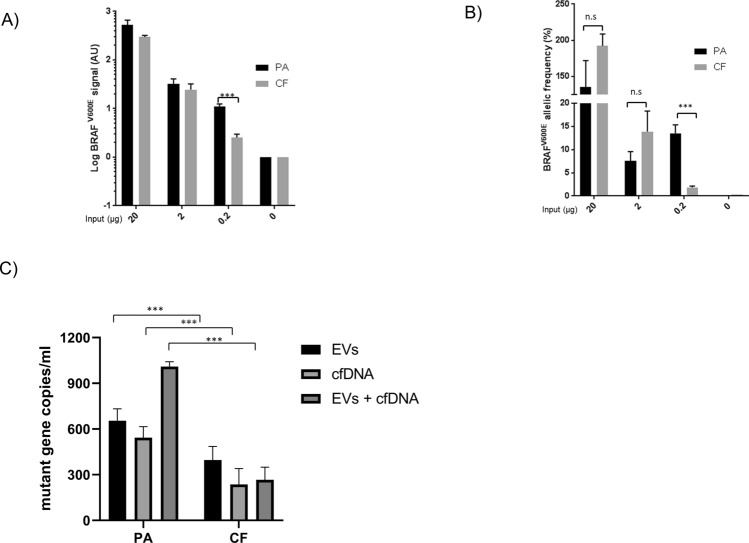
Figure 3.
Peptide-based affinity isolation improves the detection of mutant DNA from ctDNA and EVs in low-copy number samples. (A) Recovery of decreasing amounts of mutation-positive extracellular vesicles (EVs) from healthy donor (HD) plasma samples with peptide affinity (PA) isolation and cell-free circulating nucleic acid isolation protocol (CF). Following DNA extraction, BRAFV600E gene copies were detected by allele-specific quantitative PCR (AS-QPCR) and expressed as arbitrary units (AU) on a logarithmic scale. (B) BRAFV600E allelic frequency was calculated after quantifying BRAFWT gene copies by AS-QPCR and expressed as % on a logarithmic scale. Data are representative of three independent experiments. (C) Recovery of mutant DNA from both BRAFV600E-positive EVs and KRASG12S-positive cfDNA by PA and CF isolation. 2.5 µg of BRAFV600E-positive EVs and 10 nanograms of KRASG12S-positive cfDNA were spiked into HD plasma and isolated by PA and CF isolation. Following DNA extraction, mutant copies were quantified by digital PCR (dPCR). BRAFV600E gene copies and KRASG12S gene copies were considered as total mutant copies in samples where cfDNA and EVs were co-spiked in the same plasma. Results are representative of three independent experiments.