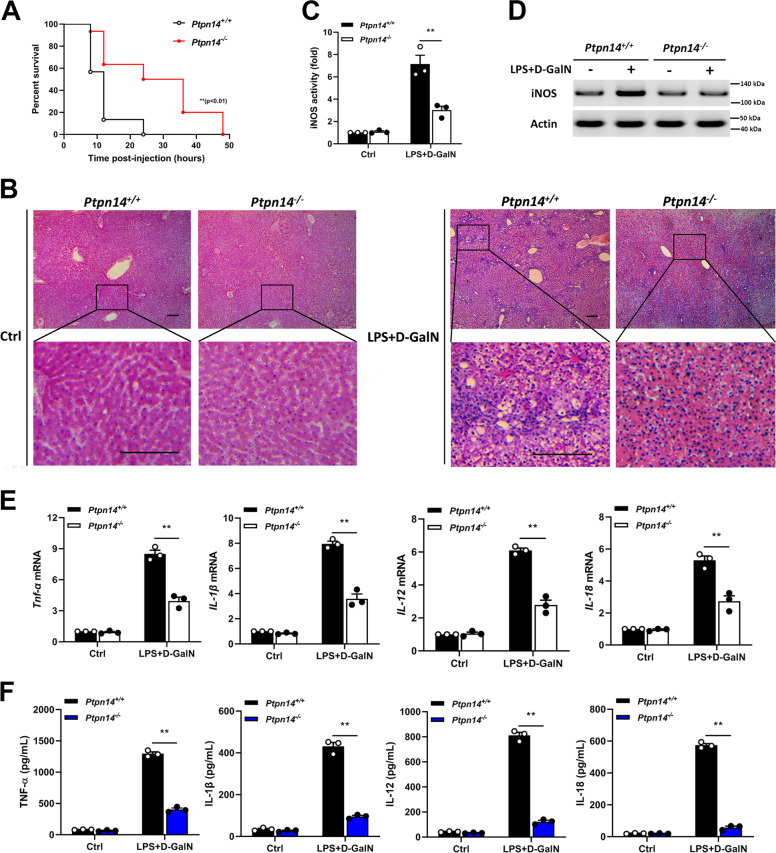
Fig. 1.
PTPN14-deficient mice show lower inflammation in acute liver failure. a Wild-type C57BL/6J mice (n = 30) and PTPN14-deficient mice (n = 30) were injected intraperitoneally with E. coli O111: B4 LPS (0.01 mg/kg) and D-GalN (800 mg/kg). Mice were observed for moribundity and lethality within 72 h. b At 20 h post-infection, livers were collected for H&E staining to observe the inflammation. Scale bar = 200 μm. c, d iNOS activity of liver tissue at 20 h post-infection. e, f qRT-PCR (e) and ELISA (f) were used to detect the expression levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-12, and IL-18 in the liver. Mouse survival data (a) were plotted as Kaplan–Meier curves and compared by log-rank (Mantel–Cox) test. Histopathology (b) and blots (d) were representatives of three independent experiments. Data shown in c and f were cumulated from three independent experiments (mean ± s.e.m. of n = 3). qRT-PCR data (e) were representative of one experiment with at least three independent biological replicates; a single data point represented one technical repeat. Two-tailed Student’s t-test was used to compare the means between two groups (c–f). **p < 0.01.