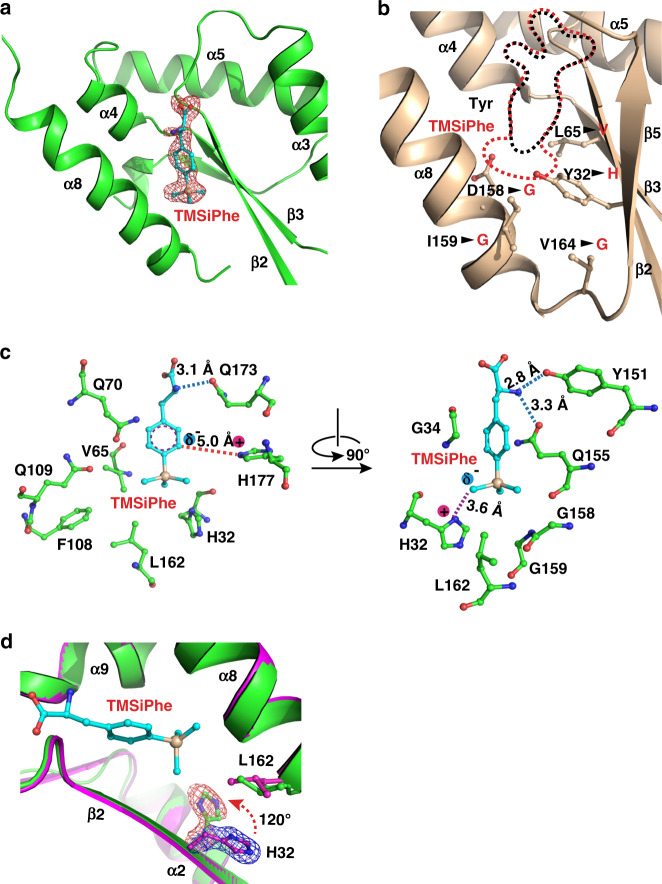
Fig. 2. Structural basis for the selective recognition of TMSiPhe by TMSiPheRS.
a Binding of TMSiPhe at the active site of TMSiPheRS. The 2Fo-Fc annealing omit electron density map of TMSiPhe was contoured at 1.0 σ. b Comparison of the unnatural amino acid-binding pockets between TMSiPheRS (red dotted line) and the wild-type Mj-TyrRS (black dotted line, PDB:1J1U). Five key mutations, indicated by arrows, increased the size of the TMSiPhe-binding pocket substantially. c Interactions between TMSiPhe and TMSiPheRS. The specific interactions include hydrogen bonds (blue dotted line), π-cation interactions (red dotted line), ion-dipole interactions (magenta dotted line) and hydrophobic interactions with surrounding residues (left panel). d The H32 residue in the β2 strand was rotated ~120 degrees in the TMSiPhe/TMSiPheRS complex (green) compared with TMSiPheRS alone (magenta), leading to favorable charged interactions with TMSiPhe. The 2Fo-Fc annealing omit map clearly shows the electron density of H32. The map was contoured at 1.0 σ.