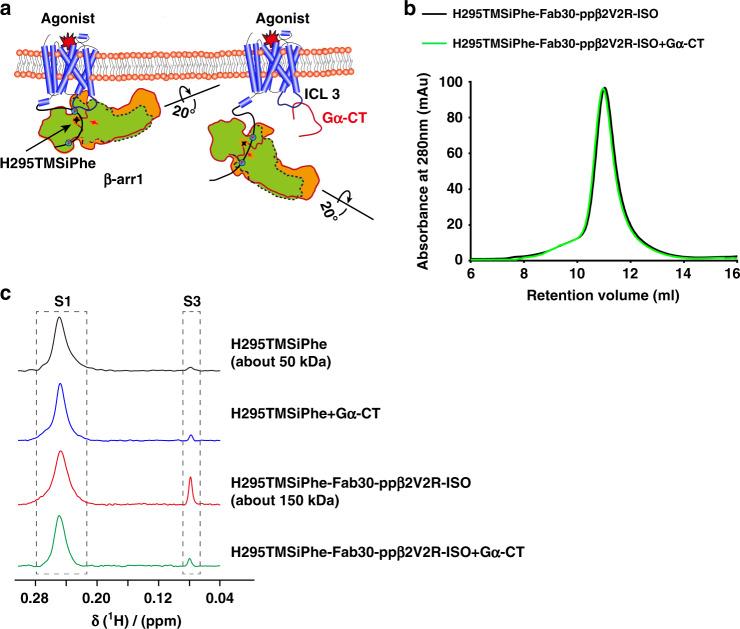
Fig. 5. Gα-CT competition experiments.
a Schematic diagram of the interaction between GPCRs and β-arr1 in the presence of excess Gα C-terminus (Gα-CT), which has been described in previous reports47. The interaction between β-arr1 and the GPCR TM core was abolished via steric hindrance by Gα-CT. β-arr1 still interacts with the phosphorylated GPCR C-terminal tail and thus forms a complex with the receptor. The blue circles indicate the phosphorylation. The Shuriken indicate the position of H295TMSiPhe in inactive (black) and active (red) β-arr1. b ISO/ppβ2V2R/β-arr1/Fab30 complex formation was not disrupted by Gα-CT in a size-exclusion assay. The similar SEC profile observed with or without Gα-CT suggests that Gα-CT did not disrupt the ISO/ppβ2V2R/β-arr1/Fab30 complex. Size-exclusion chromatography experiments were performed on an AKTA Purifier equipped with a Superdex 200 (10/300 GL) column. Black: ISO/ppβ2V2R/β-arr1-H295TMSiPhe/Fab30 complex, green: ISO/ppβ2V2R/β-arr1-H295TMSiPhe/Fab30 complex mixed with the 200 μm Gα-CT. c 1D 1H NMR spectra of β-arr1-H295TMSiPhe in the presence of Gα-CT. The transformation from S1 to S3 induced by the ISO/ppβ2V2R/β-arr1/Fab30 complex was significantly weakened by the addition of Gα-CT, suggesting the observed S3 state reduction was mainly caused to the elimination of the receptor core interaction with β-arr1 by the binding of Gα-CT.