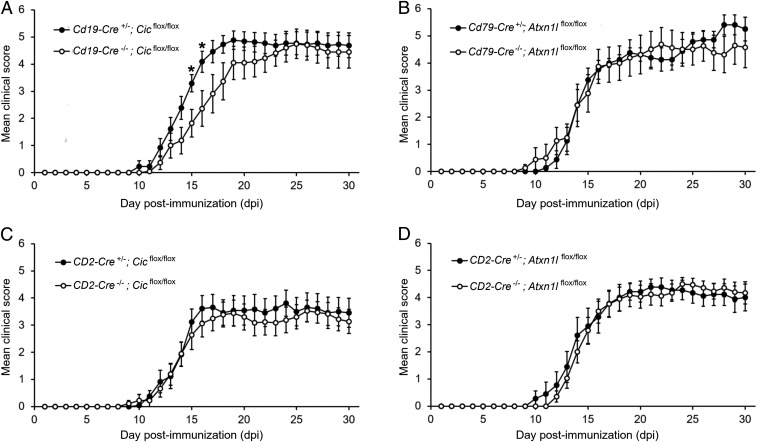
Fig. 5.
Ataxin-1 mediates its immunoregulatory function in B cells through CIC interactions. (A and B) EAE was induced in conditional knockout lines in which the ataxin-1 interactors CIC and ATXN1L were selectively ablated in the B cell lineage using B cell-specific Cre drivers (Cd19-Cre or Cd79-Cre). B cell-specific CIC-null mice showed more severe disease at peak (15 to 16 dpi) as compared to floxed littermates (Cre−/−), while no statistically significant differences were detected in the EAE course of B cell-specific ATXN1L-null animals and controls (n = 18 Cd19-Cre+/−;Cicflox/flox mice, n = 12 Cd19-Cre−/−;Cicflox/flox mice, n = 8 Cd79-Cre+/−;Atxn1lflox/flox mice, n = 8 Cd79-Cre−/−;Atxn1lflox/flox mice). (C and D) Conditional knockout lines in which CIC and ATXN1L were selectively ablated in T cells were also generated using a CD2-Cre driver. No differences in the EAE phenotype were measured in both lines as compared to their floxed littermates (n = 18 CD2-Cre+/−;Cicflox/flox mice, n = 13 CD2-Cre−/−;Cicflox/flox mice, n = 9 CD2-Cre+/−;Atxn1lflox/flox mice, n = 17 CD2-Cre−/−;Atxn1lflox/flox mice). Differences between scores in each day were assessed by two-tailed Student’s t test *P ≤ 0.05.