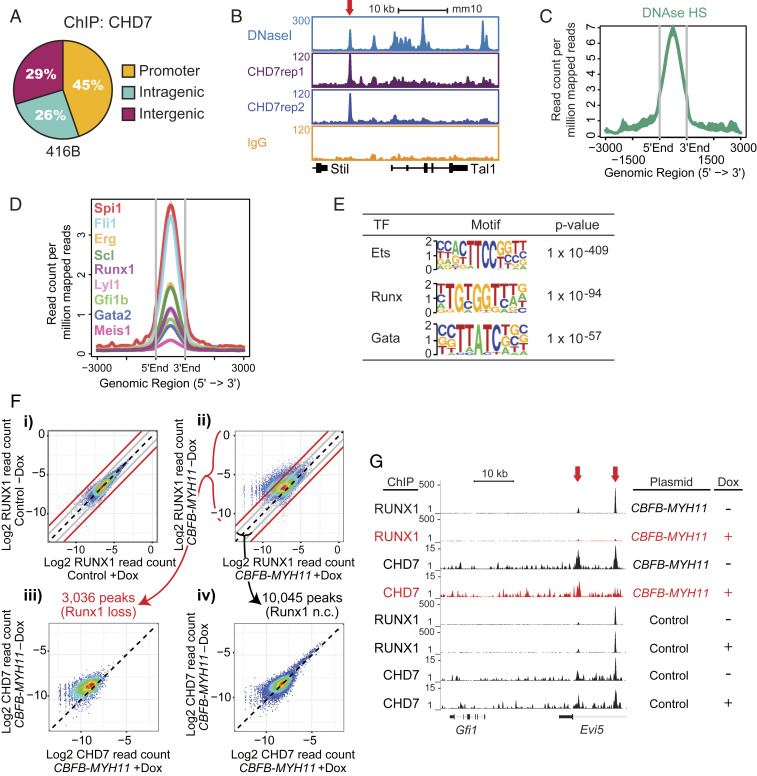
Fig. 3.
CHD7 cooperates with hematopoietic transcription factors to regulate hematopoiesis. (A) CHD7-binding distribution in the murine 416B HPC cell line by ChIP-seq. Replicates: 2. (B) Gene track of CHD7 binding overlaps with DNaseI hypersensitive sites at the Tal1 gene. (C) Overlap of CHD7-binding and DNaseI hypersensitive sites. (D) Overlap of CHD7 binding and hematopoietic transcription factors. (E) CHD7-binding sites are highly enriched for Ets, Runx, and Gata motifs by HOMER motif analysis. (F) CHD7 binding is selectively lost from genomic regions where RUNX1 binding is attenuated by CBFB-MYH11. CBFB-MYH11 expression was induced in myeloid progenitor cells by doxycycline (Dox). RUNX1 occupancy in a (i) control clone and (ii) CBFB-MYH11-expressing clone. Loss of CHD7 occupancy is (iii) higher in regions of greater than four-fold RUNX1 occupancy loss and (iv) minimally changed in regions of less than two-fold RUNX1 occupancy loss. Diagonal black lines indicate no change (n.c.). Gray lines indicate two-fold change. Red lines indicate four-fold change. A replicate experiment is shown in SI Appendix, Fig. S5B. (G) Gene tracks showing loss of RUNX1 and CHD7 binding to Evi5 (red arrows) in Dox-induced CBFB-MYH11-expressing cells.