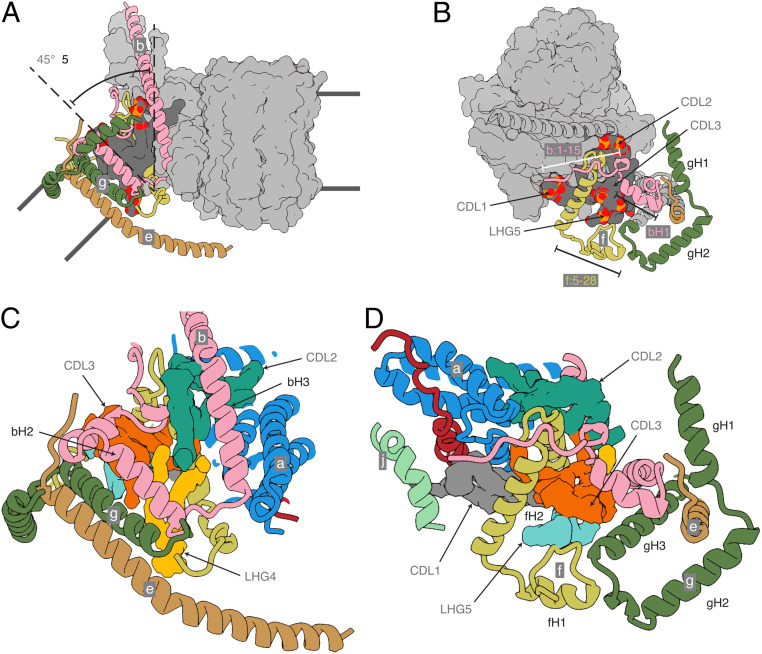
Fig. 4.
The structure of the wedge at the monomer–monomer interface in dimeric bovine ATP synthase. Subunits b, e, f, and g are pink, khaki, straw-yellow, and forest green, respectively, and subunits a, j, k, A6L, and the c8-ring are depicted as a light-gray solvent-excluded surface. The dark-gray solvent-excluded surface represents bound lipids (CDL1, CDL2, CDL3, and LHG5) with the phosphate and oxygen atoms of the head groups in orange and red, respectively. The black lines indicate the approximate boundaries of the lipid bilayer. (A) Side view of the membrane domain of the monomer showing the tilted arrangement of the transmembrane α-helices of subunits b, e, and g. (B) Top view demonstrating how the unique N-terminal topologies of subunits b, e, and g, lying in the plane of the matrix leaflet of the membrane, form part of a wedge that similarly reinforces the curvature. In addition, the transmembrane α-helix of subunit g is tilted toward the center of the dimer complex by ∼40°. (C and D) Magnified views of the same orientations of the wedge with the cryo-EM densities of the identified lipids CDL1, CDL2, CDL3, LHG4, and LHG5 in gray, turquoise, orange, yellow, and cyan, respectively. Subunits, a, A6L, and j are cornflower blue, brick red, and sea-foam green, respectively.