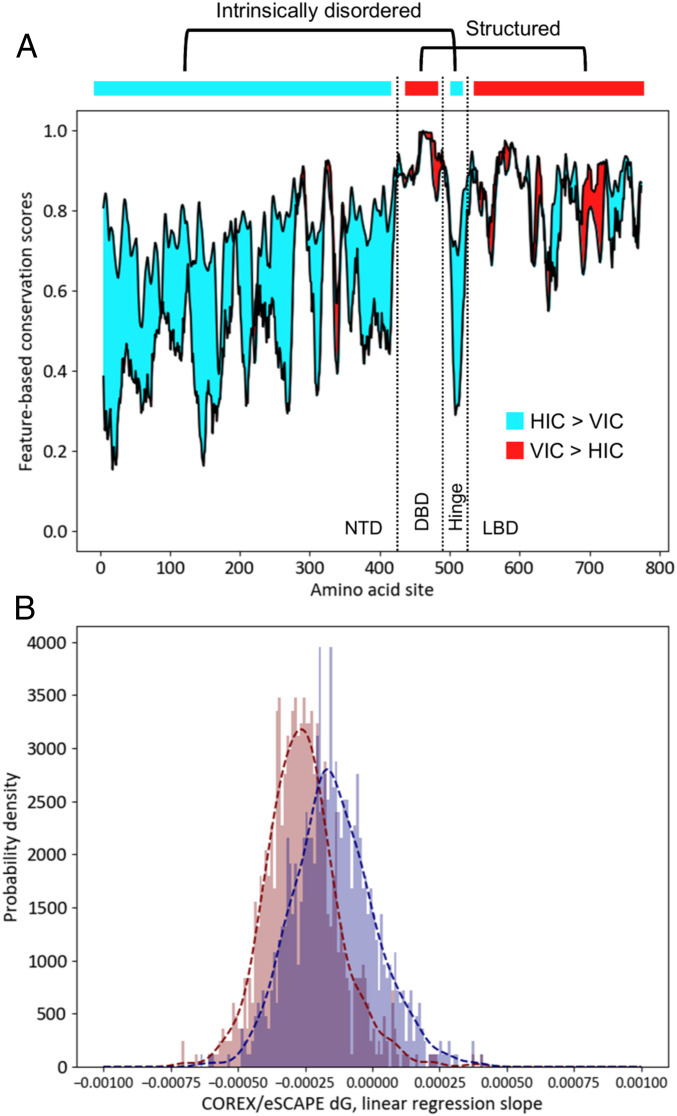
Fig. 2.
Horizontal information is more strongly conserved than vertical information in IDRs of protein families. (A) Difference between degrees of conservation of sequence and native-state free energy (ΔG, ref. 29) calculated for human glucocorticoid receptor (GR) and its orthologs (30). Cyan denotes regions where free energy conservation (HIC, horizontal information conservation) is stronger than sequence conservation (VIC, vertical information conservation), and red denotes the opposite. In human GR, the DNA binding domain (DBD) and the ligand binding domain (LBD) are structured, while the N-terminal domain (NTD) and hinge region are intrinsically disordered. Preponderance of cyan area demonstrates that horizontal information can be conserved when vertical information is not. (B) Coefficient of correlations between free energy and conservation score is calculated for ortholog alignments of 835 different transcription factors (30). Distribution of slope coefficients over many families show that sequence conservation (red) is more strongly correlated with calculated free energy, a property seen in A for a single family.