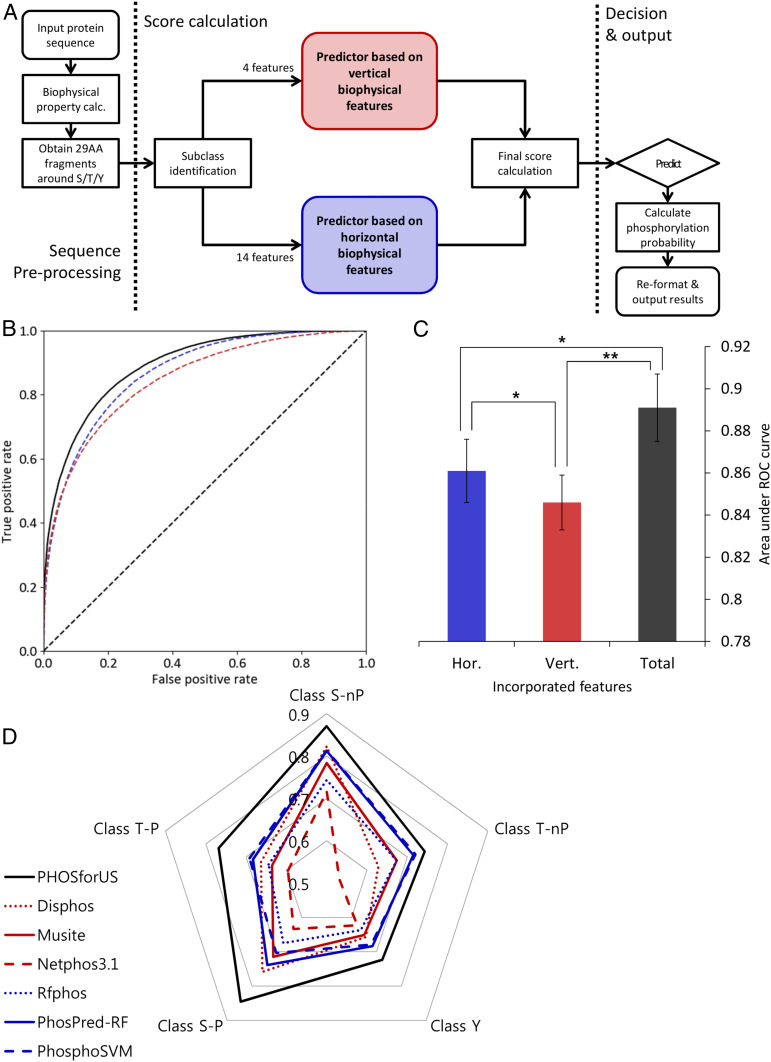
Fig. 5.
Architecture, training performance, and comparative effectiveness of the PHOSforUS predictor. (A) Simplified workflow of the PHOSforUS predictor algorithm. Biophysical properties of an arbitrary protein sequence are split into 29-mer fragments centered on Ser/Thr/Tyr residues. Five (or three) subclass-specific predictors are invoked, independently based on vertical (red) or horizontal (blue) information. Intermediate output is combined with gradient boost, and combination scores over a preset threshold are predicted as phosphorylated. (B) ROC of PHOSforUS constituent predictors. AUROC is indicated as a separate bar graph. (C) Performance of all subclasses of phosphorylation site are combined into a single curve. The combined predictor (Total, black) outperforms separate predictors based on vertical (Vert., red) or horizontal (Hor., blue) information. Notably, horizontal information significantly outperforms vertical information (C), demonstrating the importance of horizontal information. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.1. (D) Comparative effectiveness of protein phosphorylation site prediction by PHOSforUS. For five subclasses of phosphorylation site, PHOSforUS AUROC values meet or exceed those obtained on the identical data with six existing prediction tools.