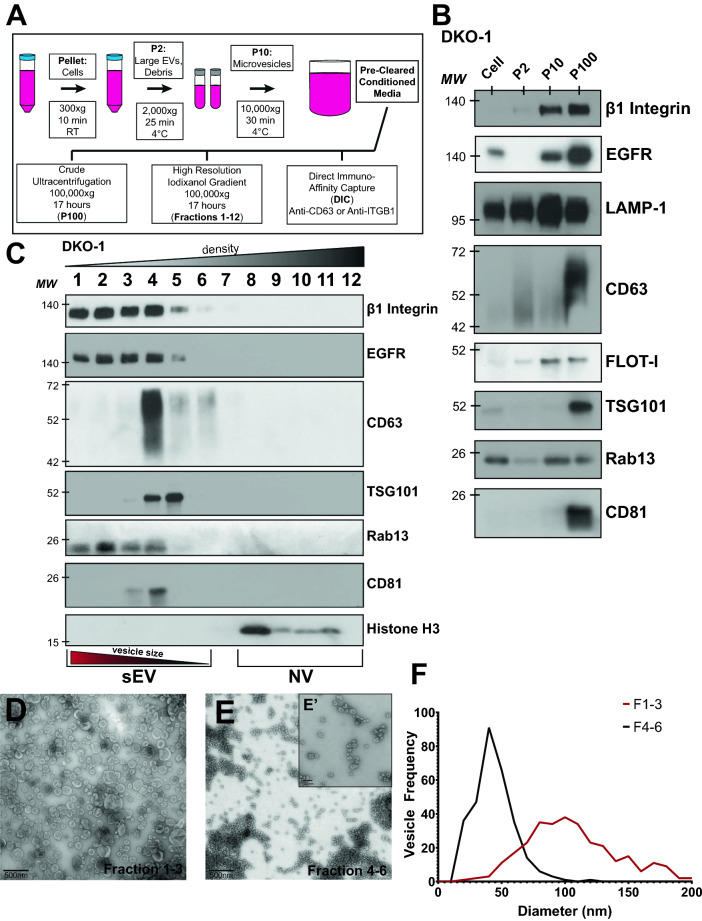
Figure 3.
Identification of β1-integrin+, Rab13 + sEVs. (A) sEV purification protocol. Conditioned media were collected from DKO-1 cells and subjected to differential centrifugation to pellet cells, large EVs, cell debris, and microvesicles, as indicated. Pre-cleared conditioned media was then subjected to one of three different isolation techniques: overnight ultracentrifugation at 100,00×g (crude sEVs), high resolution iodixanol gradient purification, or direct immuno-affinity capture. (B) Fractions described in (A) were subjected to western blot analysis using antibodies against the indicated proteins. (C) Immunoblots of sEVs and non-vesicular (NV) fractions purified from DKO-1 cells following high resolution 12–36% iodixanol gradient purification. (D) Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) of vesicles isolated by high resolution iodixanol gradients, fractions 1–3. Scale bar 500 nm. (E) Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) of vesicles isolated by high resolution iodixanol gradient purification, fractions 4–6. Scale bar = 500 nm. (E’) Higher resolution TEM image from (E) Scale bar 100 nm. (F) Vesicle sizes from the high resolution iodixanol gradients were determined and plotted. Black line corresponds to fractions 4–6 and red line corresponds to fractions 1–3. The mean diameter of the vesicles in fractions 1–3 was significantly different (p value = 2.4 × 10–79) from the mean diameter in fractions 4–6 by Student’s t test.