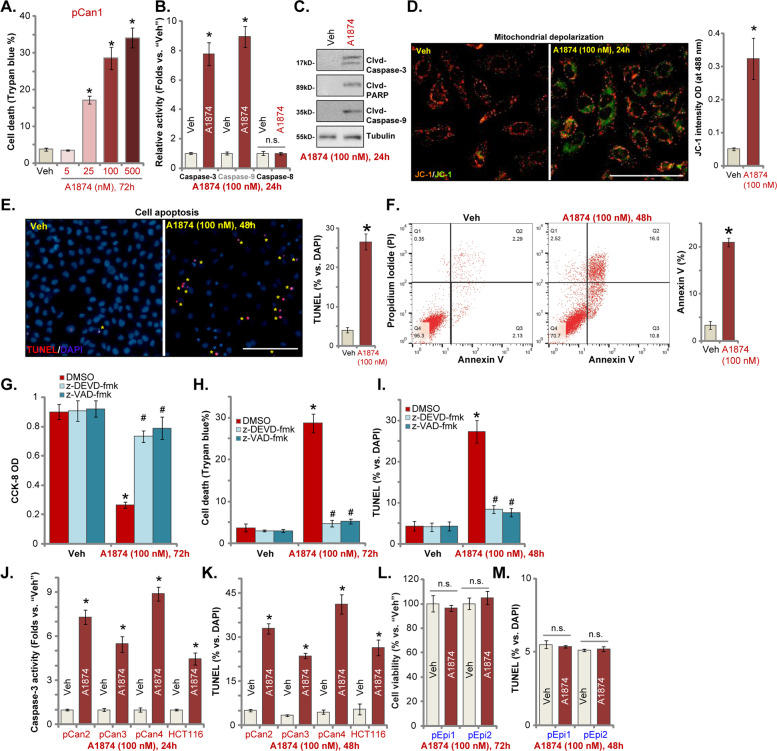
Fig. 2. A1874 induces apoptosis activation in colon cancer cells.
The primary human colon cancer cells, pCan1/2/3/4 (derived from different patients) (a–f, j, k), HCT116 cells (j, k), or primary colon epithelial cells (“pEpi1/2”) (l, m) were treated with applied concentration of A1874 (5–500 nM) or the vehicle control (“Veh”, 0.2% of DMSO). Cells were further cultured in complete medium for applied time periods. Then cell death (Trypan blue-positive cell ratio, a), caspase activation (b, c, j), mitochondrial depolarization (JC-1 green monomers intensity, d), and cell apoptosis (nuclear TUNEL staining and Annexin V FACS assays, e, f, k, m) were tested, with cell viability in epithelial cells tested by CCK-8 assay (l). The pCan1 primary colon cancer cells were pretreated with 50 μM of the caspase-3 inhibitor z-DEVD-fmk or the pan caspase inhibitor z-VAD-fmk for 30 min, followed by A1874 (100 nM) stimulation and cultured for 72 h; Then cell viability, death and apoptosis were tested by CCK-8 (g), Trypan blue staining (h) and nuclear TUNEL staining (i) assays, respectively. TUNEL-positive nuclei were marked by the yellow stars (e). Data were presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD, n = 5). *P < 0.05 vs. “Veh” cells. #P < 0.05 vs. A1874 (100 nM) only treatment (g–i). “n.s.” stands for no statistic difference (l, m). Experiments in this figure were repeated three times, and similar results were obtained. Bar = 100 μm (d, e).