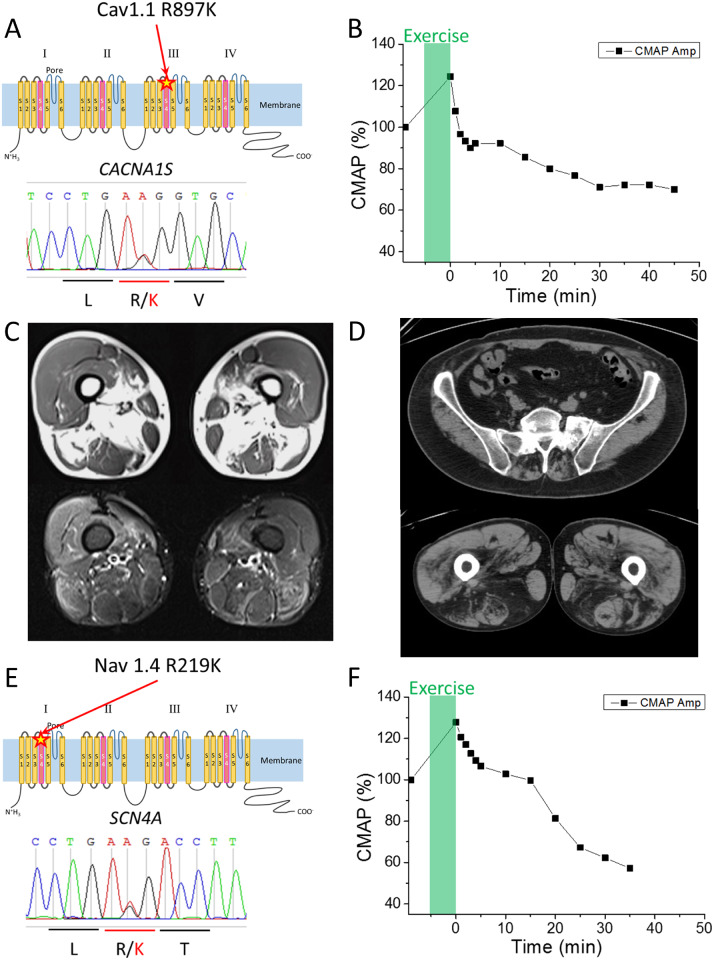
Figure 1.
Clinical information of HypoPP patients with the R/K substitution in either CACNA1S or SCN4A. (A) Schematic representation of R897K location in CaV1.1 channel (upper panel) and the result of the Sanger sequencing obtained from Case 1. (B) Prolonged exercise test in Case 1 elicited an early increase and a late decrease of ∼30% for the CMAP. (C) MRI images of skeletal muscles in Case 2-2. T1 weighted images (upper panel) and short tau inversion recovery images (lower panel) revealed fatty infiltration in soleus and medial gastrocnemius muscles. Quadriceps, gracilis, sartorius, semi-membranosus and semi-tendinosus muscles are grossly respected. (D) CT scan images of skeletal muscle in Case 3. CT scan image of lumbar portion (upper panel) showed low density area in paraspinal muscles, indicating fatty infiltration. CT scan image of thigh (lower panel) revealed low density area in bilateral hamstrings indicating fatty infiltration. (E) Schematic representation of the R219K location in NaV1.4 (upper panel) and the results of Sanger sequencing obtained from Case 4. (F) Prolonged exercise test in Case 4 revealed a decrement of the CMAP by 40%, which supports a diagnosis of periodic paralysis.