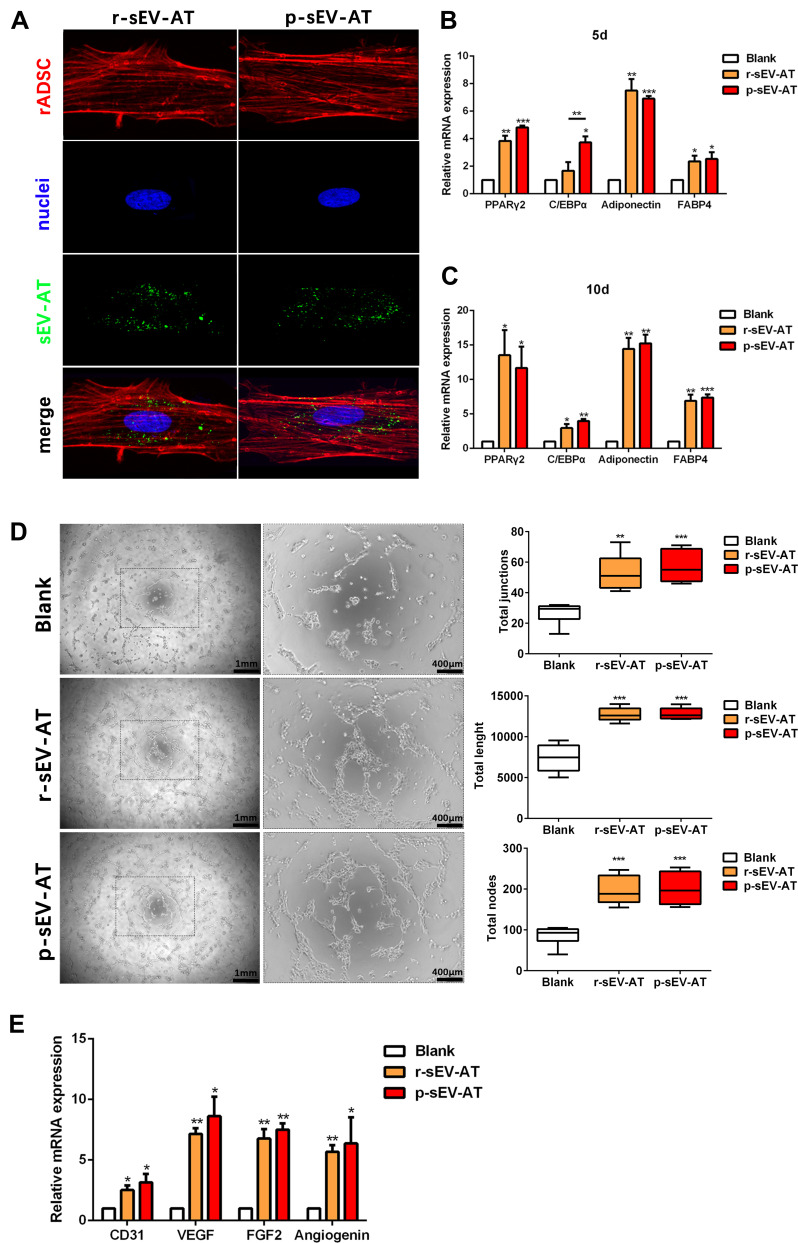
Figure 2.
The response of cultured cells to allogeneic and xenogeneic sEV-AT in vitro. (A) The morphology of rASCs and cellular uptake were detected by Fluorescence Confocal Microscopy (red: rASCs, green: sEV-AT, blue: nuclei). After co-cultured rASCs with sEV-AT for (B) 5 days or (C) 10 days, the relative expressions of adipogenic marker genes (PPARγ, C/EBPα, adiponectin and FABP4) were measured by real-time PCR (n=3). (D) Typical tube-like structures of rECs in different groups were shown (left, scar bar=1 mm, right, scar bar=400 μm), and total nodes, total junctions and total length of all tubing per field of view (scar bar=500 μm) were analyzed (n=5). (E) After co-cultured rECs with sEV-AT for 4 days, the relative expressions of angiogenic marker genes (CD31, VEGF, FGF2 and angiogenin) were measured by real-time PCR (n=3). The significance was tested with one-way ANOVA with Tukey posthoc test (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p <0.001).
Abbreviations: C/EBPα, CCAAT enhancer-binding proteins; FABP4, fatty acid-binding protein 4; FGF2, fibroblast growth factor 2; PCR, polymerase chain reaction; PPARγ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ; p-sEV-AT, small extracellular vesicles derived from porcine adipose tissue; rASCs, rat adipose-derived stromal/stem cells; rECs, rat aorta endothelial cells; r-sEV-AT, small extracellular vesicles derived from rat adipose tissue; sEV-AT, small extracellular vesicles derived from adipose tissue; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.