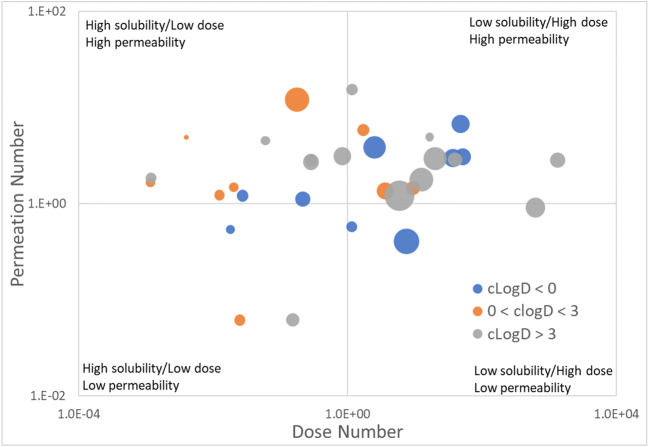
Fig. 1.
Physicochemical properties of the 30 modeled compounds. The compounds selected cover a range of solubility, permeability, molecular weight, and lipophilicity. A compound’s unitless dose number is calculated as the maximum dose administered in the food effect study in mg, divided by the FaSSIF or buffer solubility in mg/ml, and divided by an approximate small intestine fluid volume of 500 ml. A dose number greater than 1 indicates low solubility or a high dose while a dose number less than one indicates high solubility or low dose. The unitless permeation number is calculated as the effect jejunum permeability multiplied by the surface-to-volume ratio of the small intestine assuming a 1.75 cm cylindrical radius, multiplied by the small intestine transit time assumed to be 3 h. A permeation number greater than one indicates high permeability while a permeability less than 1 indicates poor permeability. The size of the markers is proportional to the active ingredient’s molecular weight. The color encodes the calculated lipophilicity