FIGURE 4.
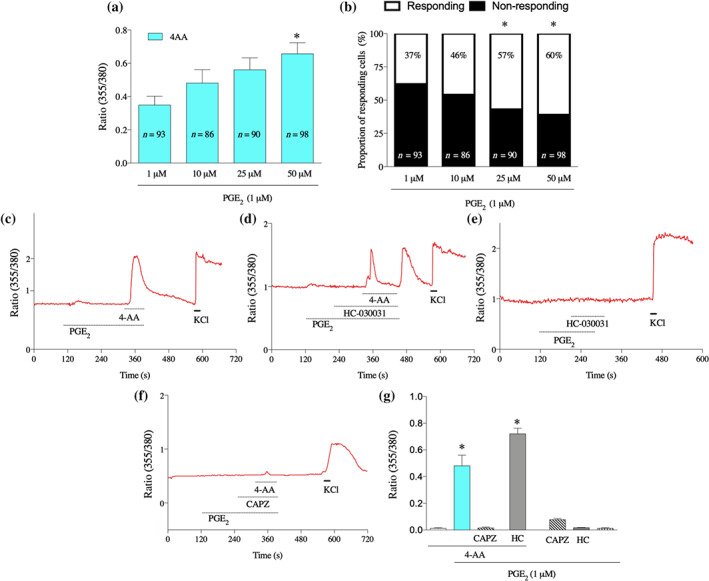
4‐AA increases [Ca2+]i through activation of TRPV1 channels in cultured primary sensory neurons following pretreatment of the cells with PGE2. (a) 4‐AA (50, 25, 10, and 1 μM) increases [Ca2+]i in primary sensory neurons, sensitised by PGE2 in a concentration‐dependent manner. (b) The proportion of 4‐AA‐responding cells is also increased following PGE2 pretreatment. *P< .05, significant effect of 4‐AA. (c–f) Representative recordings of changes in the [Ca2+]i by various conditions. Following PGE2 pretreatment, 4‐AA (50 μM) induces an increase in the [Ca2+]i in the presence of PGE2 (c). While the 4‐AA‐induced increases in the [Ca2+]i were not affected by the TRPA1 channel antagonist HC‐030031 (10 μM) in the presence of PGE2 (1 μM), at the start of washing PGE2, HC‐030031 and 4‐AA out from the recording chamber, a “buffer‐evoked” calcium transient emerged (d). Importantly, no such “buffer‐evoked” calcium transient was observed when 4‐AA was missing from the superfusate (e). The TRPV1 channel antagonist capsazepine (CAPZ; 10 μM), but not the TRPA1 channel antagonist, blocked the 4‐AA‐evoked calcium transient in the presence of PGE2 (f). (g) Average normalised amplitudes of responses of cultured primary sensory neurons in various conditions. Data shown are means SEM from a number of neurons, as follows: 4‐AA, n = 156; PGE2 +4‐AA, n = 156; PGE2+4‐AA+CAPZ, n = 142; PGE2+4‐AA+HC, n = 100; PGE2 +CAPZ, n = 115; PGE2+HC, n = 289: PGE2, n = 156. * P< .05, significant differences; one‐way ANOVA with Tukey's test
