FIGURE 4.
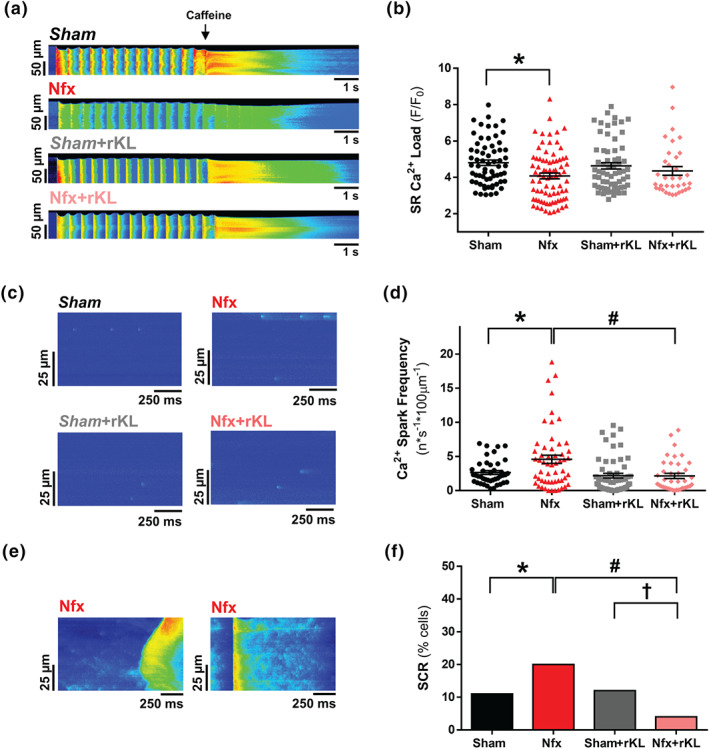
Recombinant Klotho prevents SR‐Ca2+ load and diastolic SR‐Ca2+ leak in experimental chronic kidney disease (CKD). (A) Line‐scan images of cardiomyocytes under 2‐Hz field stimulation perfused with caffeine. (B) Mean values of caffeine‐evoked Ca2+ transients amplitude expressed as peak (F/F 0) in Sham (n = 66 cells/N = 6 mice), Nfx (n = 79 cells/N = 6 mice), Sham+rKL (n = 67 cells/N = 6 mice), and Nfx+rKL (n = 49 cells/N = 6 mice) cardiomyocytes. (C) Line‐scan images of spark recordings in quiescent cardiomyocytes. (D) Mean values of Ca2+ spark frequency in Sham (1,270 sparks, n = 42 cells/N = 5 mice), Nfx (2,985 sparks, n = 55 cells/N = 6 mice), Sham+rKL (1,188 sparks, n = 56 cells/N = 5 mice), and Nfx+rKL (1,075 sparks, n = 39 cells/N = 6 mice). (E) Line‐scan images of spontaneous Ca2+ release (SCR) as Ca2+ waves (left panel) or spontaneous Ca2+ transients (right panel) in quiescent Nfx cardiomyocytes. (F) Occurrence of SCR in Sham (n = 42 cells/N = 5 mice), Nfx (n = 55 cells/N = 6 mice), Sham+rKL (n = 56 cells/N = 5 mice), and Nfx+rKL (n = 39 cells/N = 6 mice) cardiomyocytes. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. * P < 0.05, significantly different from Sham; # P < 0.05, significantly different from Nfx; and † P < 0.05, significantly different from Sham+rKL
