Figure 2.
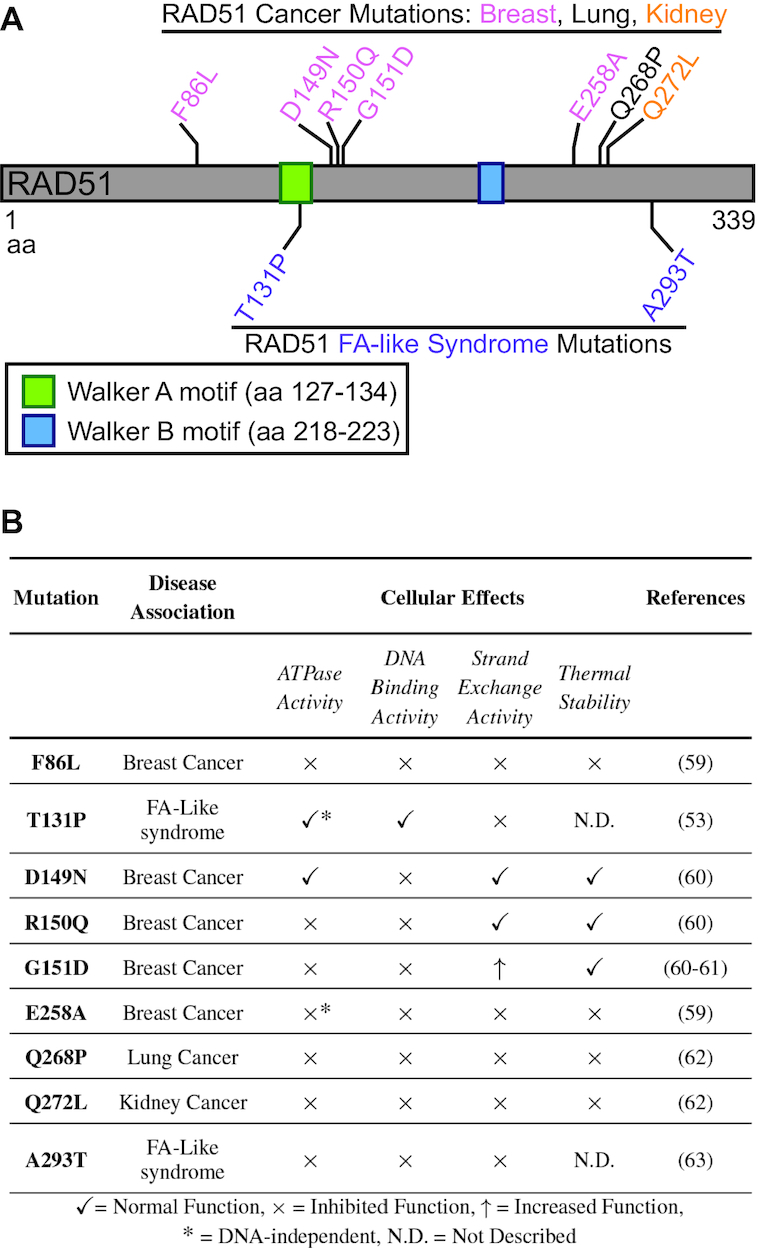
(A) Schematic of the RAD51 protein showing the Walker A and B motifs and the functionally analyzed disease-associated missense mutations. RAD51 is 339 amino acids (aa) long with Walker A and B motifs (green and blue boxes, respectively). Breast, lung and kidney cancer-associated mutations are shown in pink, black and orange, respectively. FA-like syndrome-associated mutations are shown in purple. (B) Table shows a list of the functionally analyzed RAD51 mutations that are associated with cancer or FA-like syndrome. Each mutation has been investigated for its effects on RAD51 in regard to its ATPase activity, DNA binding activity, strand exchange activity and thermal stability. A check mark indicates normal RAD51 function, an ‘x’ indicates inhibited RAD51 function, an up arrow indicates increased RAD51 function and a star indicates that ATPase activity is independent of the addition of ssDNA, unlike WT RAD51. Note that F86L, D149N, G151D, Q268P and Q272L are somatic mutations, whereas T131P, R150Q, E258A and A293T are germline mutations.
