FIGURE 7.
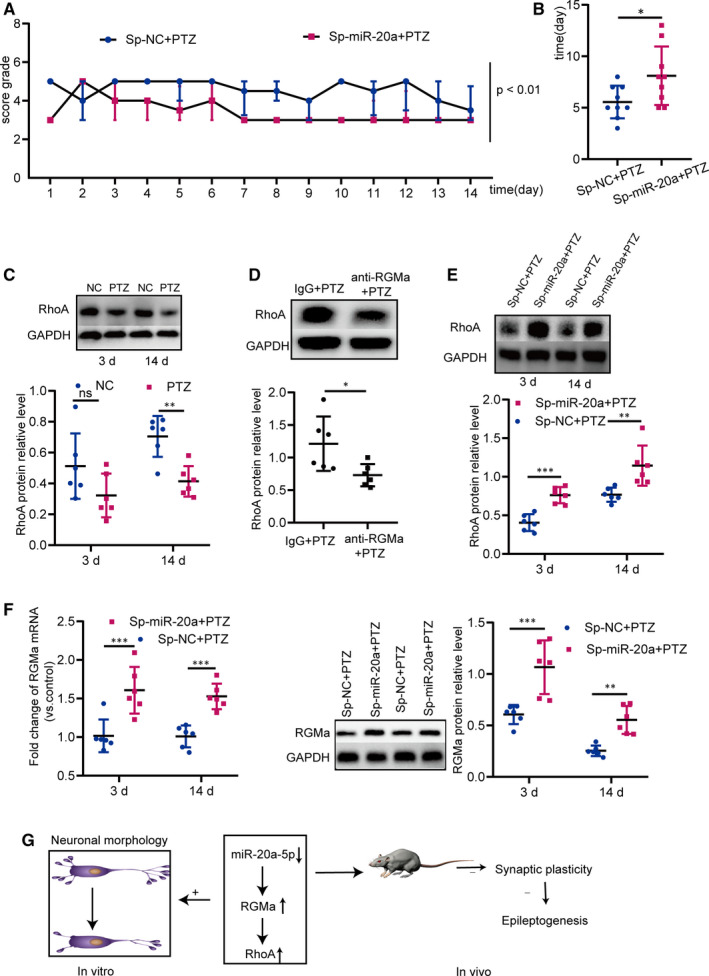
Antagonizing miR‐20a‐5p prevents epileptogenesis in the PTZ‐induced epilepsy rat model, and the miR‐20a‐5p‐RGMa‐RhoA pathway is involved in this process. A, Compared with rats in the Sp‐NC + PTZ group, antagonizing miR‐20a‐5p in Sp‐miR‐20a + PTZ rats decreased the seizure severity from 1 d to 14 d (n = 8, P < 0.01; log linear model). B, Down‐regulation of miR‐20a‐5p significantly delayed the occurrence of the first tonic‐clonic seizure (n = 8; two‐tailed t test). C, RhoA expression was distinctly lower in PTZ‐induced epilepsy rats than in control rats at 3 d and 14 d (n = 6; two‐way ANOVA, Sidak test). D, RhoA expression was significantly lower in anti‐RGMa + PTZ rats than in IgG + PTZ rats (n = 6; two‐tailed t test). E, Decreased miR‐20a‐5p increased RhoA expression in Sp‐miR‐20a + PTZ rats at 3 d and 14 d (n = 6; two‐way ANOVA, Sidak test). F, Sp‐miR‐20a + PTZ rats expressed higher RGMa mRNA and protein levels than Sp‐NC + PTZ rats at 3 d and 14 d (n = 6; two‐way ANOVA, Sidak test). G, Schematic diagram showing the mechanisms underlying miR‐20a‐5p‐RGMa‐RhoA pathway‐mediated synaptic plasticity in epileptogenesis: miR‐20a‐5p targeting RGMa regulates RhoA; down‐regulating miR‐20a‐5p reduces axonal growth and neuronal branching in vitro. Silencing miR‐20a‐5p prevents epileptogenesis through RGMa‐RhoA‐mediated synaptic plasticity in the PTZ‐induced epilepsy rat model. (ns P ≥ 0.05, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001). All data represent the mean ± SD
