Figure 3.
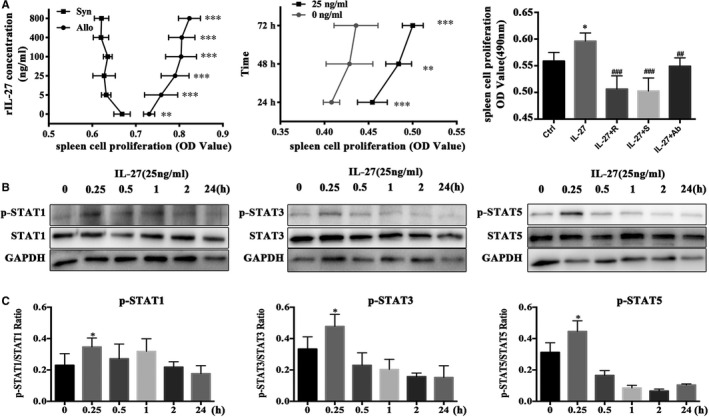
IL‐27 promoted the alloreactive spleen cells proliferation through STAT1, STAT3 and STAT5 activation. MLR were performed by syngeneic and allogeneic stimulation for 72 h. ruxolitinib (JAK inhibitor) and SH‐4‐54 (STAT inhibitor) were used to inhibit JAK/STAT activation. IL‐27 group treated with rIL‐27; IL‐27 + R group treated with rIL‐27 plus ruxolitinib; IL‐27 + S group treated with rIL‐27 plus SH‐4‐54; IL‐27 + Ab group treated with rIL‐27 and anti‐IL‐27 p28. A, First, cultured mixture splenic cells treated with different concentration of rIL‐27 for 72 h. Second, 25 ng/mL rIL‐27 was added to cultured mixture splenic cells for 24, 48 and 72 h. The third, cultured mixture splenic cells treated with rIL‐27 (25 ng/mL), rIL‐27 + ruxolitinib (0.12 µmol/L) and rIL‐27 + SH‐4‐54 (1.5 µmol/L), respectively for 72 h. Finally, CCK8 was added to wells, continue to culture for another 2 h and OD value (490 nm) was measured. B and C, The phosphorylation and total protein expressions of STAT1/3/5 pathway in different times for mixture splenic cells detected by Western blot (B) and analyzed by ImageJ (C). *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001 vs Control group. # P < .05, ## P < .01, ### P < .001 vs IL‐27 group
