FIGURE 1.
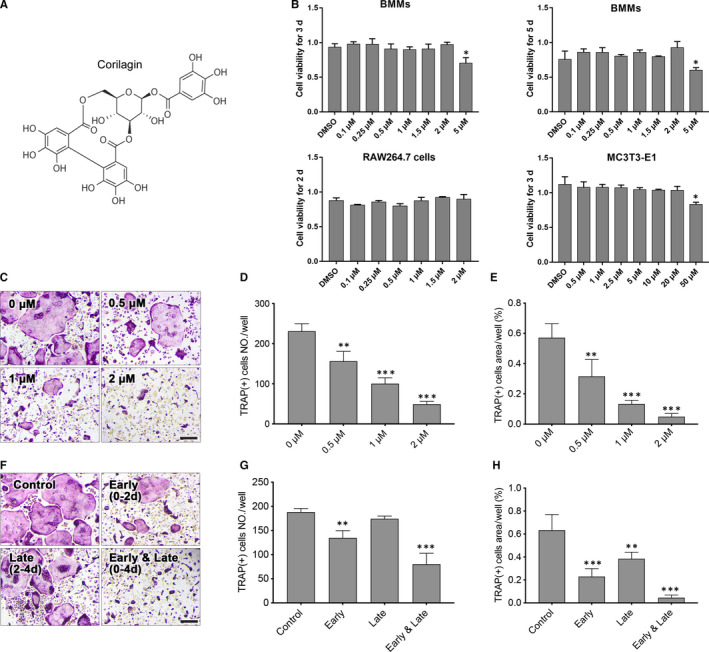
Corilagin suppressed RANKL‐induced osteoclastogenesis in vitro. A, The chemical structure of corilagin. B, The cell viability of Corilagin‐treated BMMs, RAW264.7 and MC3T3‐E1 cells was quantified by the CCK8 assay. C‐E, After treated with different concentrations of Corilagin (0, 0.5, 1, 2 μmol/L) in osteoclast medium for 4 d, TRAP staining was used to measure the number and area of mature osteoclasts. F‐H, BMMs were treated with 2 μmol/L Corilagin in the presence of 50 ng/mL M‐CSF and 100 ng/mL RANKL for 0‐2 d (early stage), 2‐4 d (late stage) or 0‐4 d (early and late stage), the numbers and area of osteoclasts were measured. Scale bar = 200 μm. All results were presented as mean ± SD. *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001 vs the control group
