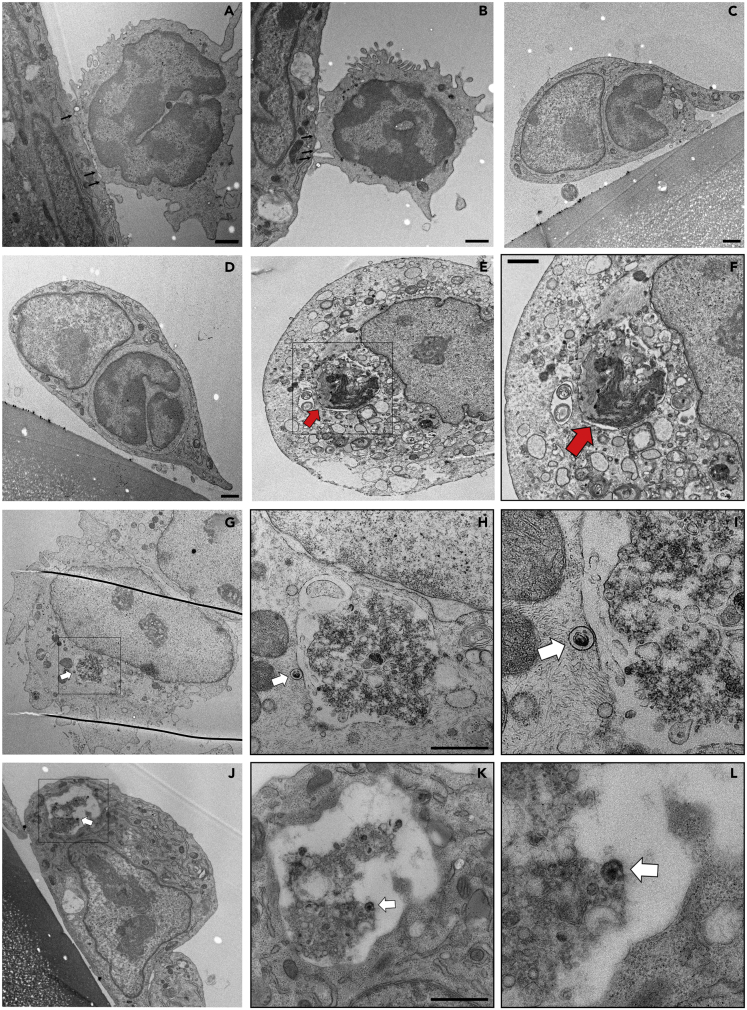
Figure 5.
Transcellular Migration of Infected-PBMC through Endothelial Cells
(A–L) Ultrathin cross sections of PBMC adherent to and crossing endothelial cells. PBMC were infected for 5 min with EHV-1 RFP and incubated over adherent EC for 3 h. Multiple intracellular protrusions invaginating the apical endothelial membrane (A and B; black arrows) and PBMC migrating through the endothelial cells (C) are shown. Intact PBMC is shown within the cytoplasm of EC (D–F; red arrow). Migrating PBMC (E) is marked with a rectangle and further magnified (F, red arrow). Partially digested infected PBMC is shown (G–L) and marked with a rectangle, which is magnified (H–I and K–L). Virus particles attached to migrating PBMC (either outside, H and I, or inside, K and L) are marked with white arrows. Scale bar, 1 μm. See also Figures S10 and S13.