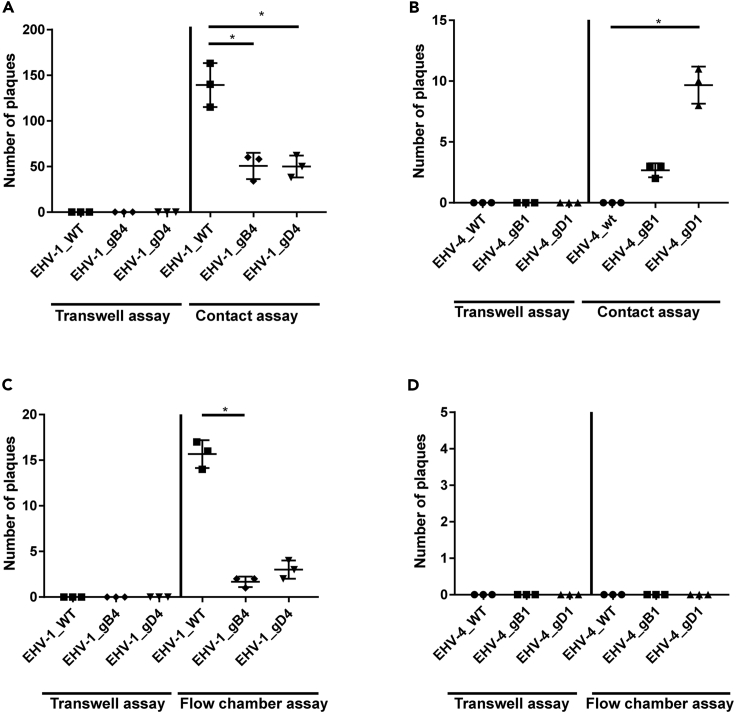
Figure 7.
Role of Viral gB and gD in Virus Transmission
(A–D) PBMC were infected with the indicated viruses (MOI = 0.1) for 5 min. Infected PBMC were overlaid on EC under “static” conditions (A and B) or allowed to flow over EC “dynamic” (C and D) in the presence of neutralizing antibodies. After 24 h, virus spread was assessed by counting the plaques on EC. As a control, infected PBMC were placed into a transwell insert without direct contact between EC and PBMC “no contact.” The data represent the mean ± standard deviation of three independent and blinded experiments. Significant differences in plaque numbers were seen between the different viruses as indicated. One-way ANOVA test followed by Dunnett's multiple comparisons test (B) or Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunns multiple comparisons test (A and C); ∗p < 0.05. See also Figure S12.