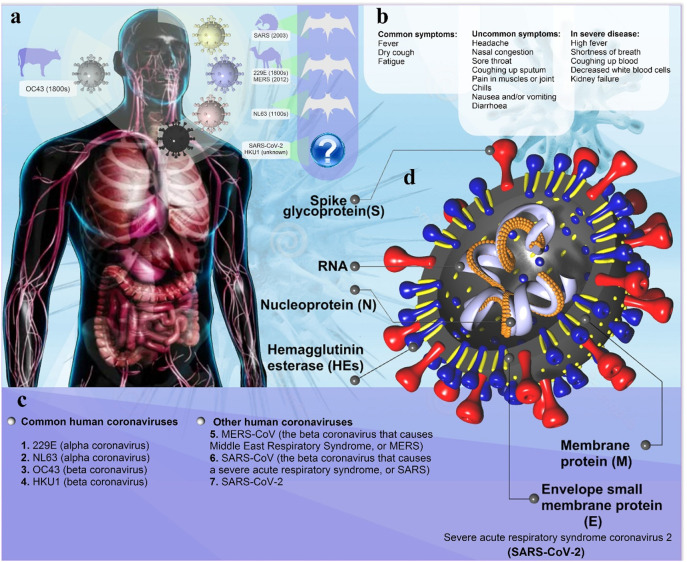
Fig. 1.
Coronavirus pathophysiology. (a) Animal (natural and intermediate hosts) origin of human coronaviruses; Pangolins may be intermediate hosts for transmission of the new SARS-CoV-2 from bats to humans. Although cats can be infected with the SARS-CoV-2, and can spread it to each other, dogs have only a low susceptibility to this virus. However, the existence of intermediate animal host(s) of SARS-CoV-2 is still likely. (b) Clinical presentation of patients with SARS-CoV-2, including common, uncommon, and severe symptoms of SARS-CoV-2. (c) Human Coronavirus Types: common human coronaviruses; 229E (alpha coronavirus), NL63 (alpha coronavirus), OC43 (beta coronavirus), HKU1 (beta coronavirus) and other human coronaviruses; MERS-CoV (the beta coronavirus that causes Middle East Respiratory Syndrome, or MERS), SARS-CoV (the beta coronavirus that causes the severe acute respiratory syndrome, or SARS), SARS-CoV-2 (the novel coronavirus that causes coronavirus disease 2019, or COVID-19); d) Diagram of coronavirus virion structure showing genome and structural proteins: spike (S), envelope (E), membrane (M), and nucleocapsid (N).