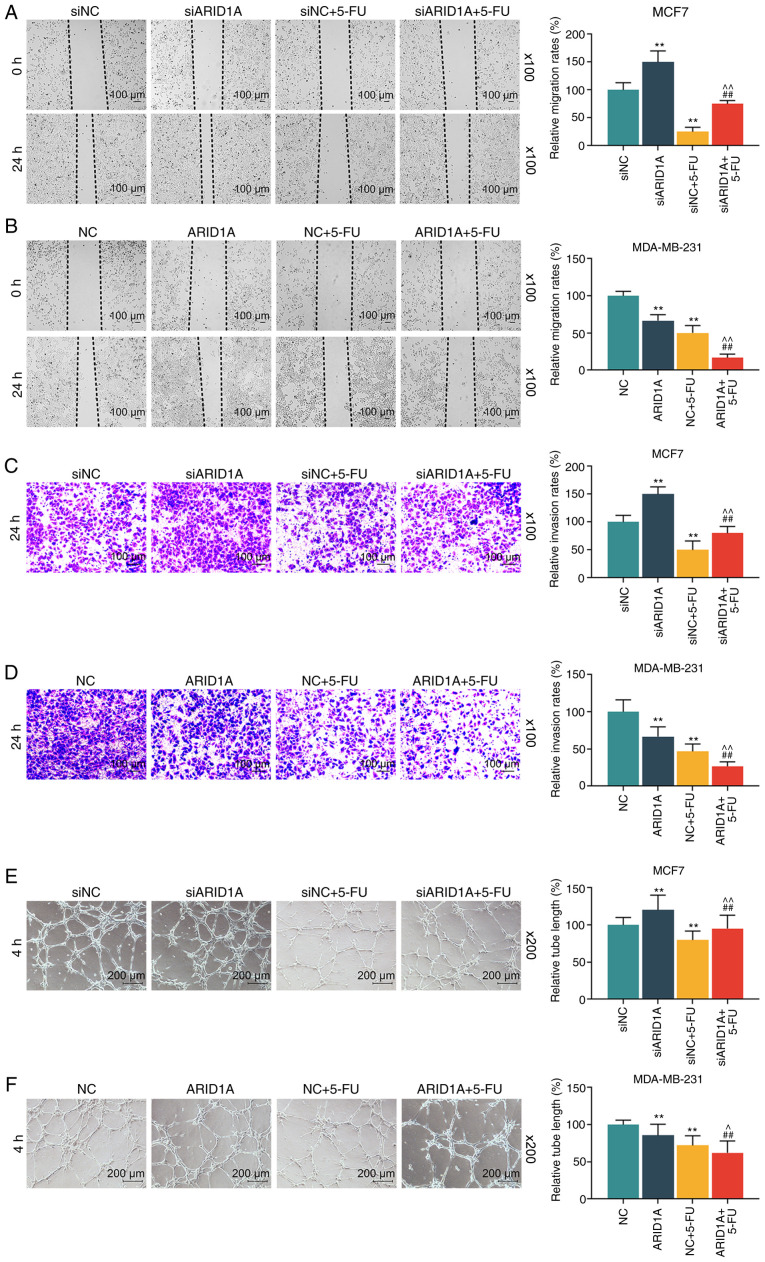
Figure 4.
Effets of ARID1A on the migration, invasion and angiogenesis of breast cancer cells treated with 5-FU. (A and B) Detection of the migration rates of MCF7 and MDA-MB-231 cells following transfection with siARID1A or pCMV6-XL4-ARID1A and treatment with 40 µg/ml 5-FU by wound healing migration assay at 0 and 24 h. (C and D) Measurement of the invasion rates of MCF7 and MDA-MB-231 cells following transfection with siARID1A or pCMV6-XL4-ARID1A and treatment with 40 µg/ml 5-FU by invasion assay at 24 h. (E and F) Detection of the angiogenesis formation rates of MCF7 and MDA-MB-231 cells following transfection with siARID1A or pCMV6-XL4-ARID1A and treatment with 40 µg/ml 5-FU by tube formation assay. Data were obtained from 3 representative experiments and are presented as the means ± standard deviation. The experiment was repeated 3 times (n=3). **P<0.001 vs. siNC or NC; ##P<0.001 vs. siARID1A or ARID1A; ^P<0.05, ^^P<0.001 vs. siNC + 5-FU or NC + 5-FU. ARID1A, AT-rich interactive domain 1A; 5-FU, 5-fluorouracil.