Figure 2.
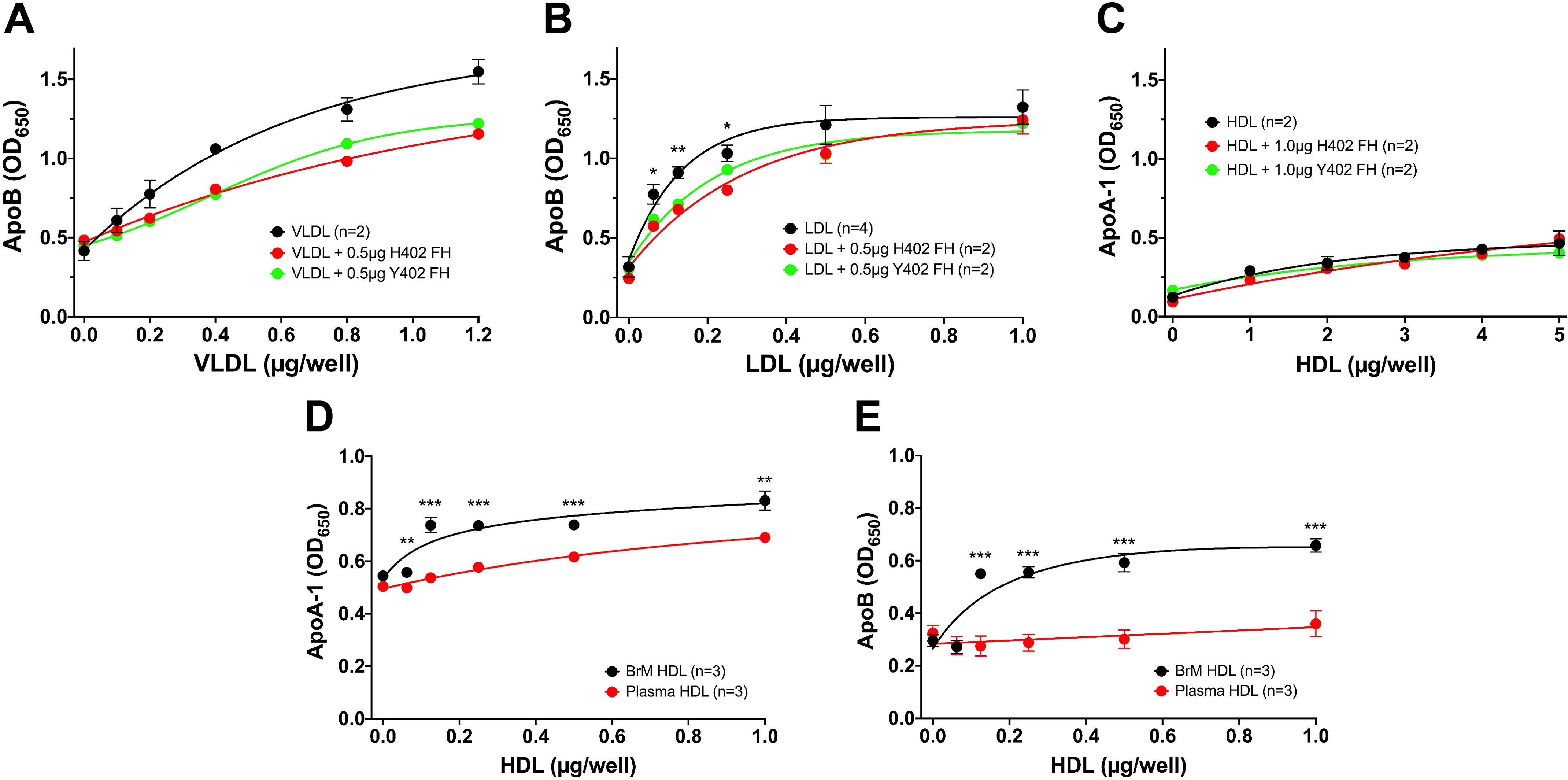
Measurement of lipoprotein binding to porcine RPE-derived ECM. A 96-well binding assay with primary porcine RPE cell ECM-coated wells was used to measure plasma lipoprotein binding to porcine RPE-derived ECM. A, VLDL binds well to the ECM, as measured by the ApoB bound on the plate. Each concentration point of VLDL alone was measured in duplicate, and the VLDL binding when mixed with 0.5 μg of each variant of FH was an individual point. This assay was repeated with similar results using 1 μg of each FH variant (see Fig. S2). B, LDL also binds well to this ECM (n = 4), and this binding can also be inhibited equally by both the “risk” variant of FH, His-402 (n = 2), and the normal Tyr-402 (n = 2). This experiment was repeated with 1.0 μg of FH with similar results. C, plasma-derived HDL does not bind well to the ECM, and FH has no effect on the binding as measured by ApoA-1 binding. This assay had n = 2 for each point. This assay was repeated with HDL at a concentration range of 0–1 μg and 1 μg FH, and similar results were seen. D and E, comparisons of HDL isolated from BrM tissue and from plasma from the same donor reveal that the BrM-derived HDL bound better to the RPE-derived ECM compared with the same concentration of plasma-derived HDL, as measured by both ApoA-1 (D) and ApoB (E) binding, suggesting that at least some of the BrM lipoprotein particles contain both ApoA-1 and ApoB. Error bars, S.D. Very small errors did not produce visible error bars. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001. OD, optical density.
