Figure 2.
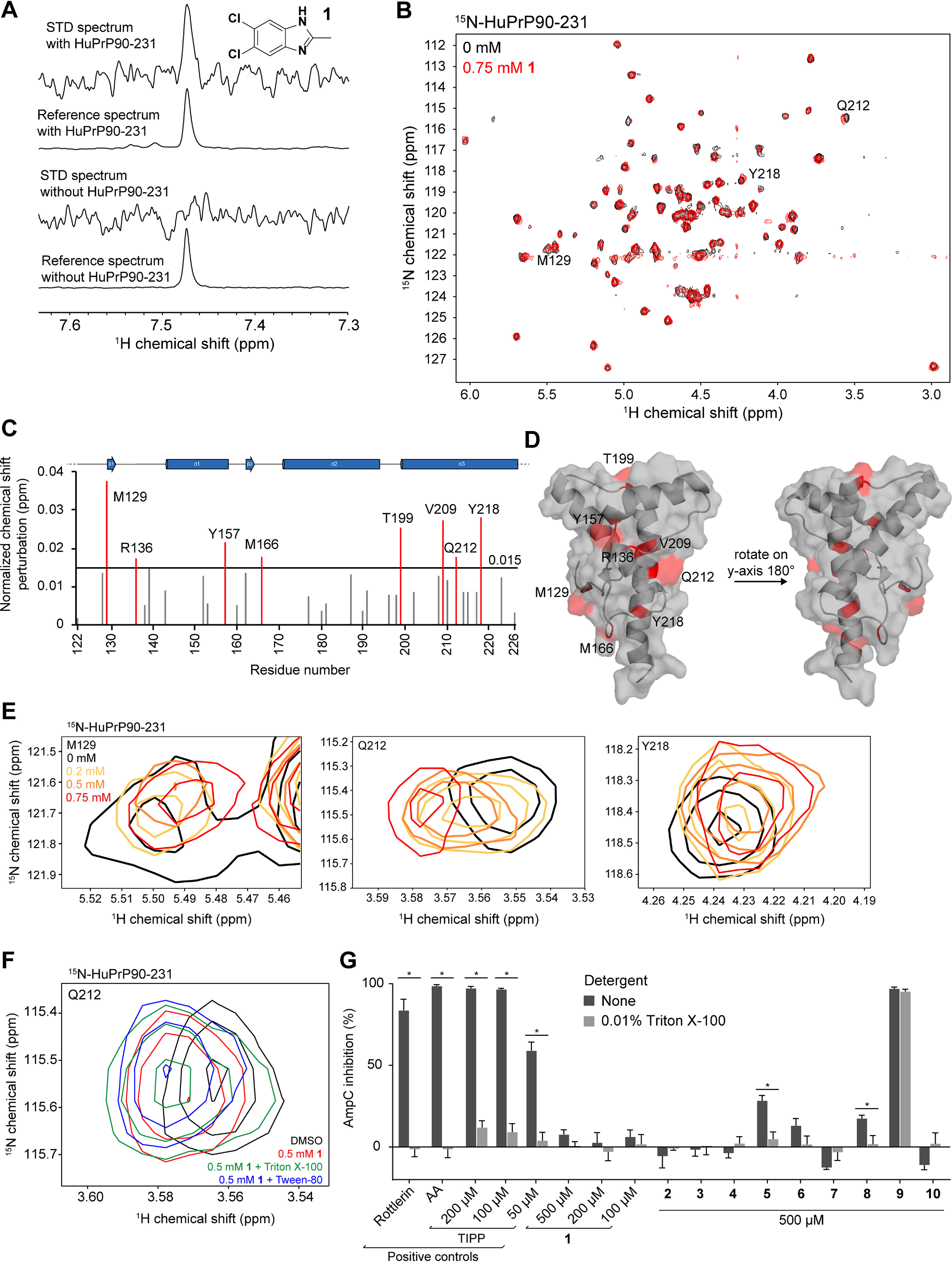
Validation and characterization of a benzimidazole fragment hit. A, STD NMR spectra of 1 (5,6-dichloro-2-methyl-1H-benzimidazole) with and without HuPrP90-231. STD spectra are scaled to 16× the reference spectra. B, TROSY spectrum of 15N-HuPrP90-231 with DMSO (black) or 0.75 mm 1 (red). Peaks that shift greater than 0.015 ppm are denoted with the residue number. C, normalized chemical shift perturbations upon addition of 0.75 mm compound 1. D, residues that shift more than 0.015 ppm were mapped onto the NMR structure of PrP (PDB entry 1HJM) (63). E, concentration-dependent CSPs of residues Q212, M129, and Y218 upon addition of 1. F, 1H-15N TROSY chemical shifts in the presence of 0.75 mm 1 with and without detergents. G, AmpC inhibition assay of 1 and its analogs. Rottlerin (10 μm), anacardic acid (AA, 10 μm), and tetraiodophenolphthalein (TIPP) are prototypical aggregators. Adding detergent to small-molecule aggregates dissociates them and attenuates inhibition of AmpC. *, significance cutoff between detergent and nondetergent tests was p < 0.01 after correction for multiple comparisons. Data are means ± S.D. of four intrarun technical replicates performed on the same microplate.
