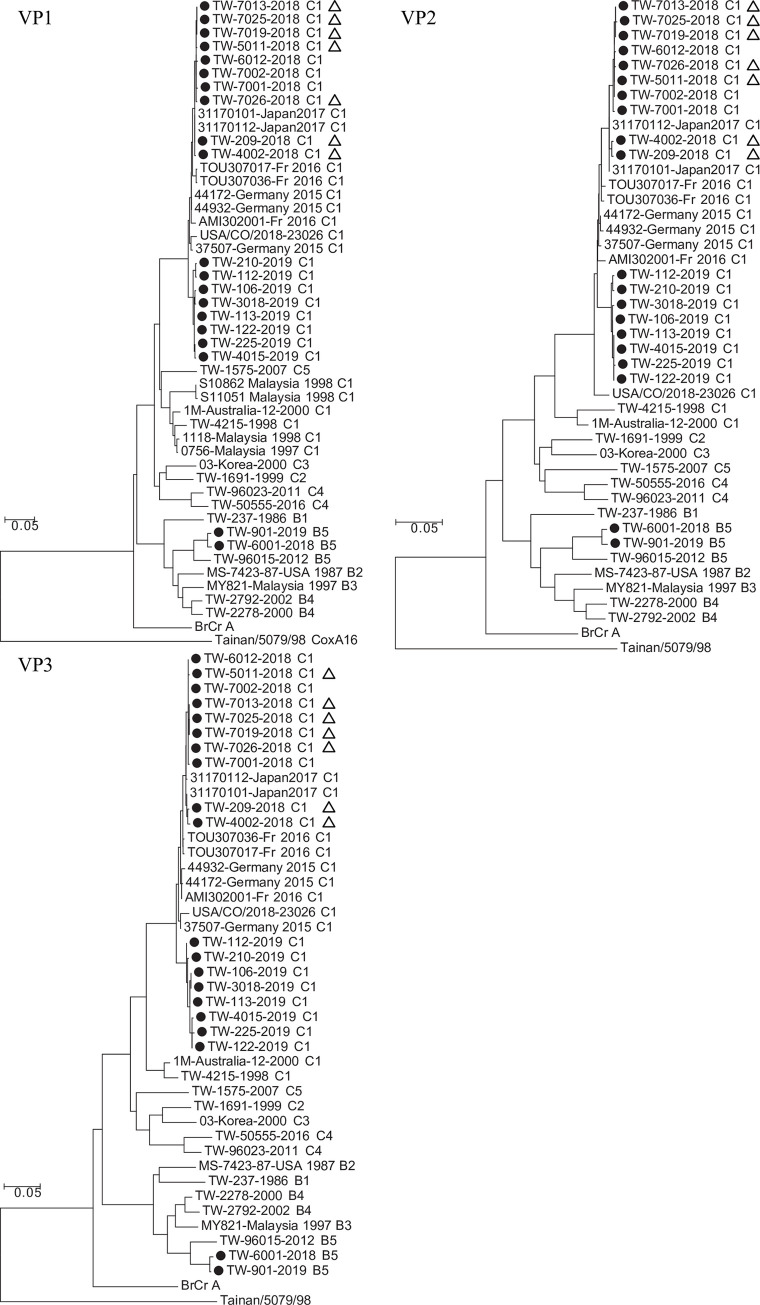
Fig 1. Phylogenetic tree of the EV-A71 isolates identified between 2018 and 2019 in Taiwan.
Phylogenetic analyses were based on viral protein VP1, VP2 and VP3 nucleotide sequences of the Taiwan EV-A71 isolates identified between 2018 and 2019 (black circles) and a representative set of EV-A71 and enterovirus isolates (891 bases for VP1, 762 bases for VP2, 726 bases for VP3). The 2018–2019 EV-A71 that were isolated from patients with severe neurological manifestations were labeled with open triangles (refer to S1 Table). Trees were constructed by using the neighbor-joining method with 1,000 replicates through MEGA 7.0.25 (http://www.megasoftware.net/). Coxsackievirus A16 strain Tainan/5079/98 (AF177911.1) was used as the outgroup. The distances were computed using the Maximum Composite Likelihood method and are in the units of the number of base substitutions per site. Genotype assignment, country, and year of isolation are provided in the virus names. TW, Taiwan.