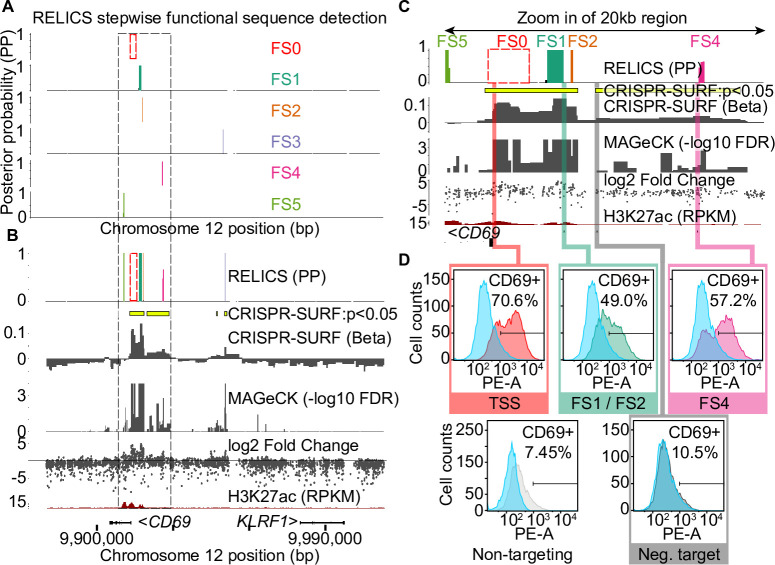
Fig 3. Analysis of a published CRISPR activation (CRISPRa) screen for CD69 expression in Jurkat T cells.
(A) RELICS detects 5 functional sequences (FSs) labeled FS1-FS5. FS0 is a known positive control sequence (the CD69 promoter) provided as input to RELICS and CRISPR-SURF. (B) Analysis of the CD69 screen by RELICS, CRISPR-SURF, MAGeCK and log2 fold change. The RELICS probabilities for each FS are collapsed into a single track. An H3K27ac ChIP-seq track for Jurkat cells is included. (C) Zoom in of a 20kb region (indicated by dashed box in (a) and (b)). Experimentally tested regions are indicated by colored bars. (D) Experimental validations. Lentiviruses carrying sgRNAs targeting different regions were transduced to Jurkat cells expressing dCas9:VP64, and the expression of CD69 was measured by flow cytometry using PE-conjugated anti-human CD69 antibody. The results from each experiment are overlaid those from a non-targeting negative control sgRNA (blue). Targeting sgRNAs were chosen for their high specificity and high predicted efficiency (relative to possible sgRNAs in the region) and in some cases are adjacent to the predicted FS rather than within the FS. Results from additional validation experiments are shown in S6 Fig.