Figure 2.
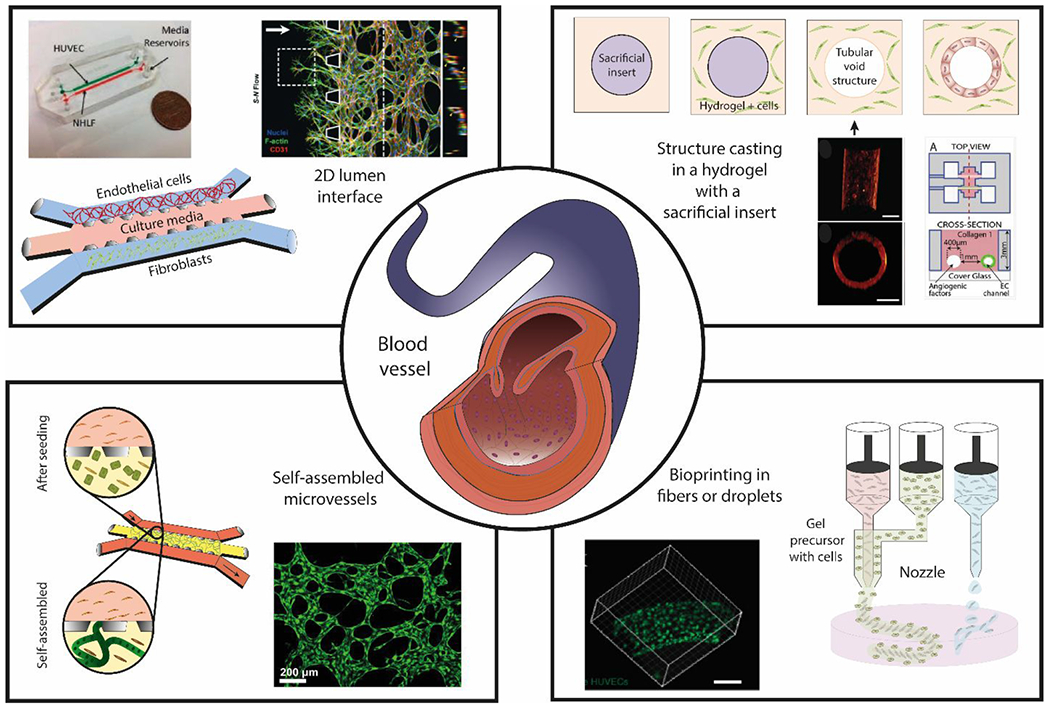
Overview of blood vessel structure and different approaches to generate microfluidic lumen-based systems. (Center) Schematic representation of a blood vessel in vivo. (Top-left) generation of 2D lumen interfaces using 3 parallel channels in contact with each other defined by capillary valves. Cells are seeded in the channels without a supporting matrix. (Top-right) Structure casting of luminal structures embedded in a hydrogel with a sacrificial insert29. (Bottom-left) Microvessel self-assembly of endothelial cells within a fibrin hydrogel in the presence of supporting cells. (Bottom-right) Bioprinting of fibers or droplets. Copyright (2013) National Academy of Sciences for top-right images, ref 32. Microscopy image at bottom-right is reproduced from ref. 182 with permission from the WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim, copyright 2014. Top left is reproduced from ref 59 with permission from Oxford University Press, copyright 2013. 21, 29, 32, 59, 225
