Figure 20.
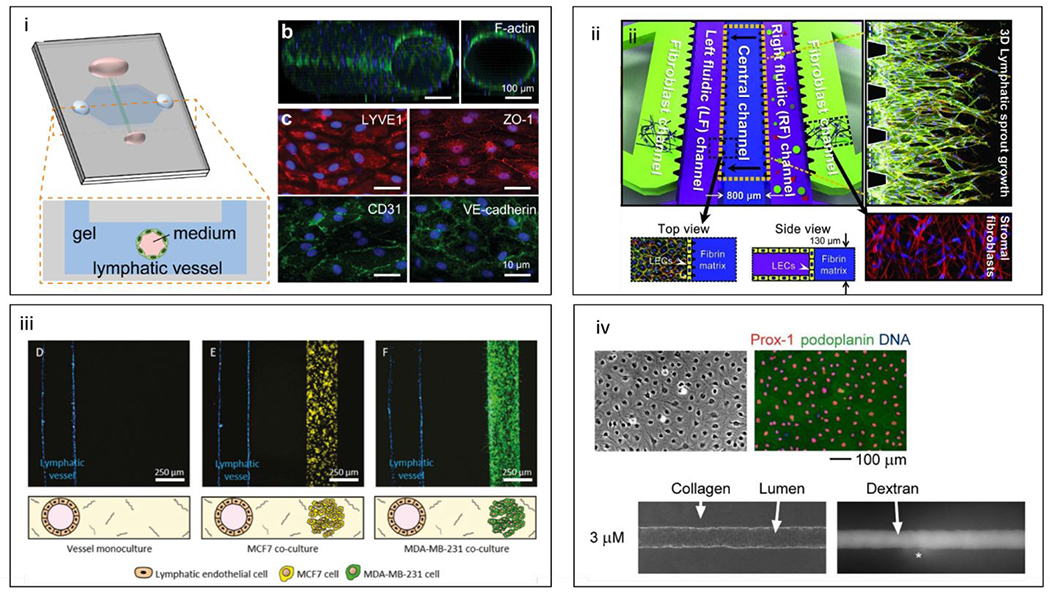
Microfluidic lymphatic models, (i) Schematic of organotypic lymphatic vessel model. A lymphatic endothelial tube is formed in natural hydrogel by removing a sacrificial mold. (b) Confocal image of a cultured lymphatic vessel with patent tubular structure. (c) Lymphatic vessels express lymphatic vessel endothelial hyaluronan receptor 1 (LYVE1) and endothelial junctional proteins (ZO-1, CD31, and VE-cadherin).211 (ii) Schematic of multi-microchannel device comprising outer channels for stromal fibroblasts, a central channel for ECM, and two inner channels for lymphatic endothelial patterning or biochemical gradient generation. Top and side views of the lymphatic and ECM channels are included for clarification, along with immunofluorescent images of lymphatic vessel sprouting and stromal fibroblasts.209 (iii) Adaptation of the microfluidic lumen model shown above for lymphatic-breast cancer co-cultures. Representative images of vessel monoculture, coculture with MCF7 cells (in yellow), and coculture with MDA-MB-231 cells (in green).212 (iv) LEC cultures and tubes. Lymphatic markers Prox-1 (red) and podoplanin (green) and DNA (blue)(top). Phase-contrast image of LEC tubes cultured under 3 μM db-cAMP and fluorescence images after 26 minutes of perfusion with Alexa 488-conjugated 10 kDa dextran (bottom).210 Reproduced with permission from Elsevier: from ref. 209, copyright 2016; from reference 210, copyright 2008.
