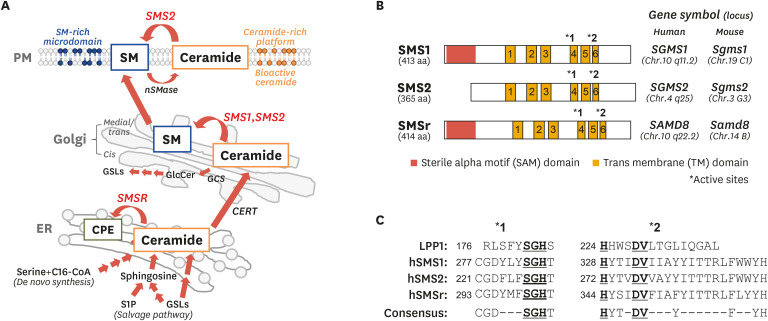
Fig. 2. Intracellular generation of ceramide and SM, and characterization of SMSs.
(A) SM synthesis from ceramide by SMS and its cellular compartmentalization. Ceramide is generated through de novo synthesis or salvage pathway in ER and is subsequently transported to the Golgi apparatus by CERT. In the Golgi, ceramide is the substrate of SMS1 and SMS2 that catalyze SM synthesis while it is used for GlcCer production by GCS. Synthesized SM is transported and distributed to intracellular membranes including PM. In addition, SM is also generated from ceramide by SMS2 on the PM. Membrane SM forms SM-rich microdomains and plays a role in numerous cellular signaling pathways. However, membrane SM is hydrolyzed by neutral nSMase to ceramide, which acts as a bioactive lipid or forms ceramide-rich platforms to regulate signaling. (B) Structure and gene symbols of SMS1, SMS2, and SMSr. Asterisks indicates LPP consensus motif in (C). (C) Alignments of LPP consensus motifs in human LPP1 and SMSs. Underlined amino acids indicate residues responsible for catalytic activity.
SM, sphingomyelin; SMS, sphingomyelin synthase; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; CERT, ceramide transfer protein; GlcCer, glucosylceramide; GCS, glucosylceramide synthase; PM, plasma membrane; SMase, sphingomyelin by sphingomyelinase; lipid phosphate phosphatase; C16-CoA, palmitoyl-CoA; GSL, glycosphingolipid; S1P, sphingosine 1-phosphate.