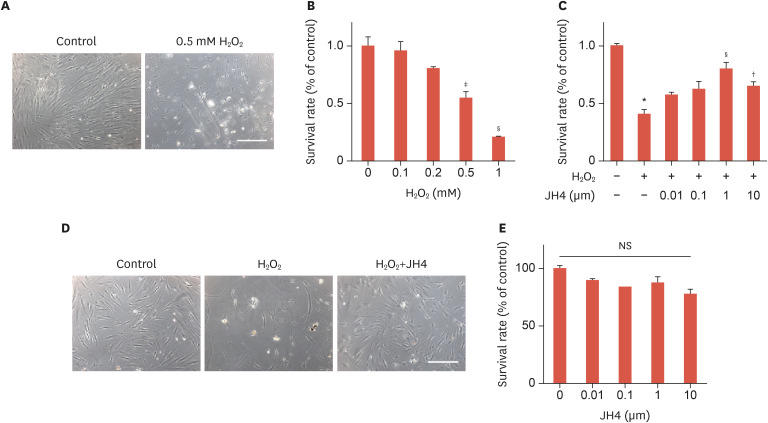
Fig. 1. Effects of JH4 pretreatment on the H2O2-induced cell death of ASCs. (A) H2O2-induced cell death of ASCs. ASCs were treated with 0.5 mM H2O2 or vehicles for 48 hours, and cell images were taken under microscope. (B) Dose-dependent effects of H2O2 on cell viability of ASCs. ASCs were treated with the indicated concentrations of H2O2 for 48 hours, and cell viability was measured using the MTT assay. (C) Effects of JH4 on H2O2-induced cell death of ASCs. ASCs were pretreated with the indicated concentrations of JH4, treated with 0.5 mM H2O2 for 48 hours, followed by measurement of cell viability. (D) Effects of JH4 on H2O2-induced morphological change of ASCs. ASCs were treated with 0.5 mM H2O2 for 48 hours in the absence or presence of 1 μM JH4, followed by capturing cell images. (E) Effects of JH4 on cell viability of ASCs. ASCs were treated with the indicated concentrations of JH4 for 48 hours, followed by measurement of cell viability. The data represent the mean ± standard error of the mean. Scale bar, 200 μm.
H2O2, hydrogen peroxide; NS, not significant; ASC, adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cell; MTT, 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide.
*p<0.001 vs. control; †p<0.05; ‡p<0.01; §p<0.001 vs. H2O2 only by 1-way analysis of variance.