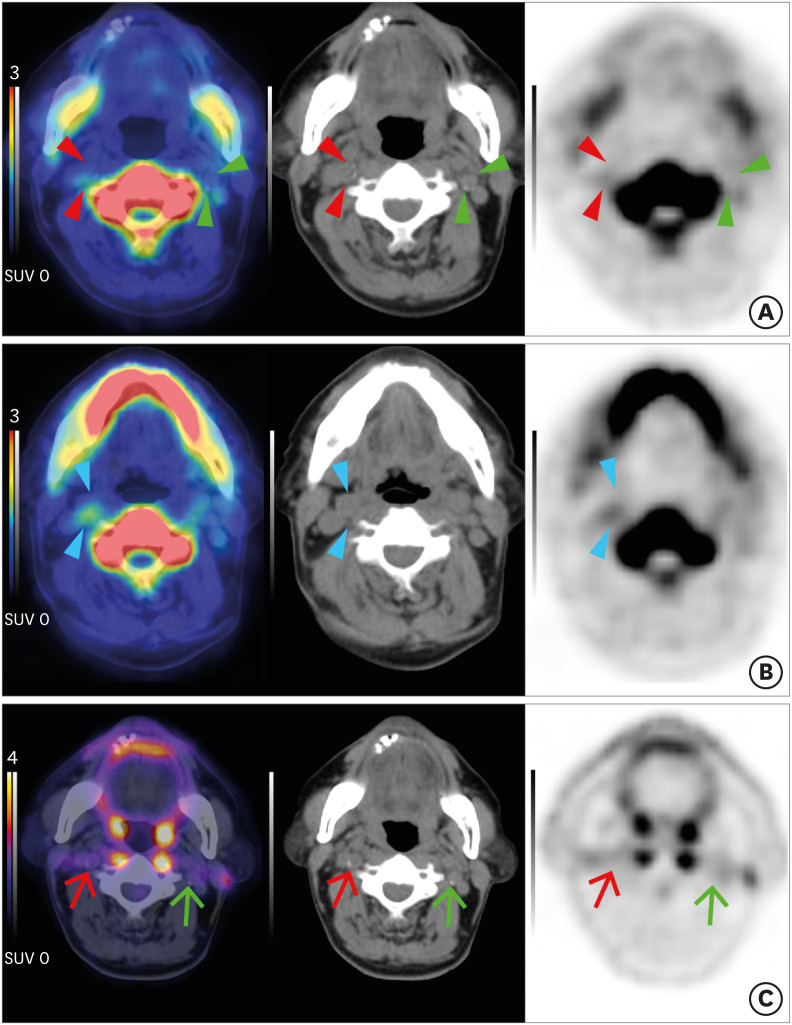
Fig. 2. Carotid plaques of a patient with acute stroke on Na[18F]F PET and [18F]FDG PET. A 77-year-old man with acute stroke in the right centrum semiovale, corona radiata, and superior frontal lobe due to total occlusion of the right proximal ICA. NaF (A, B) and FDG (C) PET/CT fusion (left), CT (middle), PET (right) axial images. (A) A low-attenuating culprit plaque showed focal Na[18F]F uptake in the right ICA on fusion PET/CT, CT, and PET images (red arrowheads). In contrast, left focal calcified asymptomatic carotid plaque did not exhibit Na[18F]F uptake (green arrowheads). (B) Note that more prominent Na[18F]F uptake was shown in the non-calcified portion of the culprit plaque (blue arrowheads). (C) In both culprit (red arrows) and non-culprit (green arrows) plaques, [18F]FDG uptake was not significantly increased. Images from our institution.
Na[18F]F, sodium fluoride; PET, positron emission tomography; FDG, fluorodeoxyglucose; ICA, internal carotid artery; CT, computed tomography.