Fig. 2. Representative clinical images of this cohort demonstrate broad range of severity across multiple genotypes.
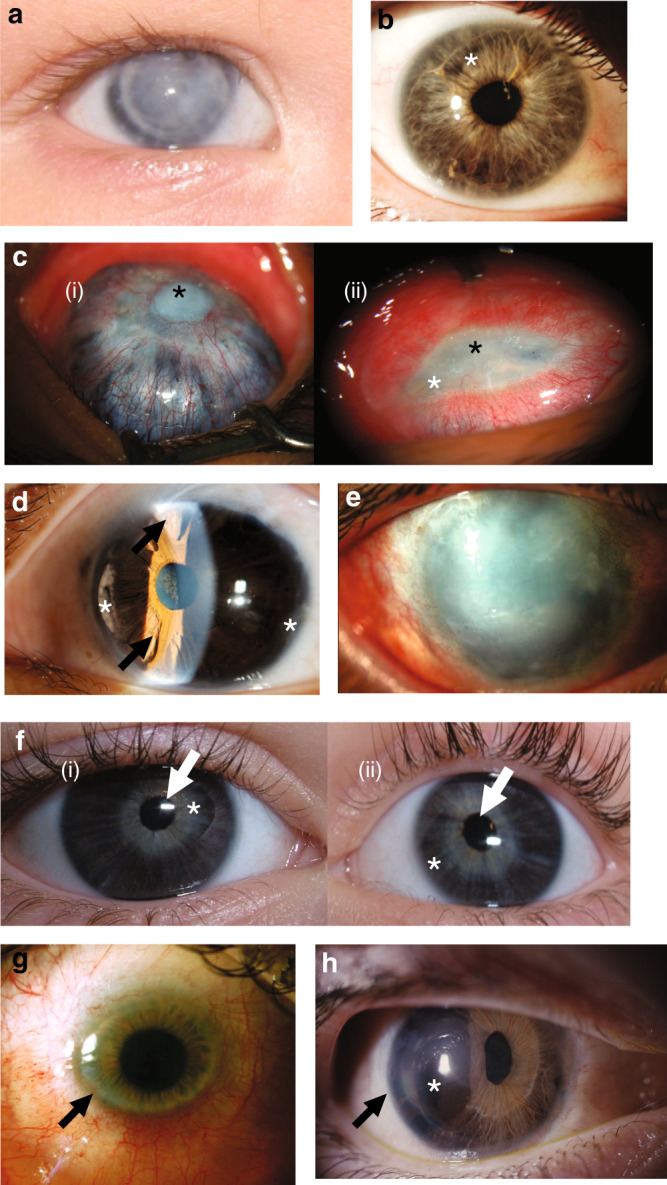
a Patient 26 with COL4A1 heterozygous variant. Photograph of right eye with Peters anomaly and failed corneal graft. b Previously undiagnosed affected mother of patient 26, with right eye showing mild features of anterior segment disorder (ASD) including Rieger anomaly, with strands of iris adhesions to the overlying cornea and mild iris hypoplasia (white asterisk). c Patient 21 with PXDN homozygous variant. Right eye (i) has previously undergone penetrating keratoplasty at age 4 years. Now failed corneal graft with central corneal opacity (black asterisk). Scleromalacia surrounding this with choroidal tissue visible through the residual sclera. Left eye (ii) shows sclerocornea with a residual small oval opaque central corneal tissue (black asterisk) with injected and dilated superficial corneoscleral vessels. No clear view of iris structures through cornea. d Patient 9 with homozygous variant in ADAMTS17. Left eye slit lamp view of anterior segment demonstrating features of Axenfeld–Rieger anomaly: corectopia, polycoria (arrows), peripheral iridocorneal adhesions, anterior iris stroma hypoplasia (white asterisk). ( e) Patient 30 with CYP1B1 variants: left eye shows generalized corneal opacification. In addition, surgical scarring is visible superiorly from previous glaucoma filtration surgery. f Patient 28 with CPAMD8 variants: right (i) and left (ii) eyes of proband showing corectopia of pupils (white arrows) and iris hypoplasia with the iris sphincter muscle visible (white asterisk). g Patient 36 with PITX2 heterozygous variant: image shows the clinical features of primary congenital corneal opacification, commonly termed sclerocornea. This case has central area of clear cornea, which on corneal topography has low (flat) keratometry in the range meeting definition of cornea plana. The peripheral cornea is scleralized (arrow) making identification of the peripheral iris difficult as well. h Patient 14 with PITX2 heterozygous variant: image shows features of Axenfeld–Rieger anomaly with iris hypoplasia (asterisk), corectopia, polycoria, and posterior embryotoxon (black arrow).
