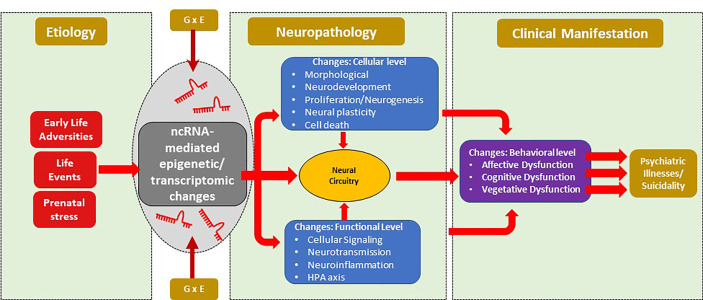
Figure 3.
Schematic diagram of the non-coding RNAs’ impact on psychiatric illnesses and suicidality. Risk factors for mental illnesses include early life adversity, current or recurrent life events that along with gene environment interaction can lead to epigenetic modifications mediated by ncRNAs. These modifications can give rise to neuropathology mediated by changes at cellular and/or molecular levels, which can subsequently alter neural circuitry. Phenotypic changes can arise from circuitry changes that can mediate the development of psychiatric illnesses such as major depression, bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Suicidal behavior could be a manifestation of psychiatric illnesses or may be independent of psychiatric illnesses. ncRNAs, non-coding RNA.