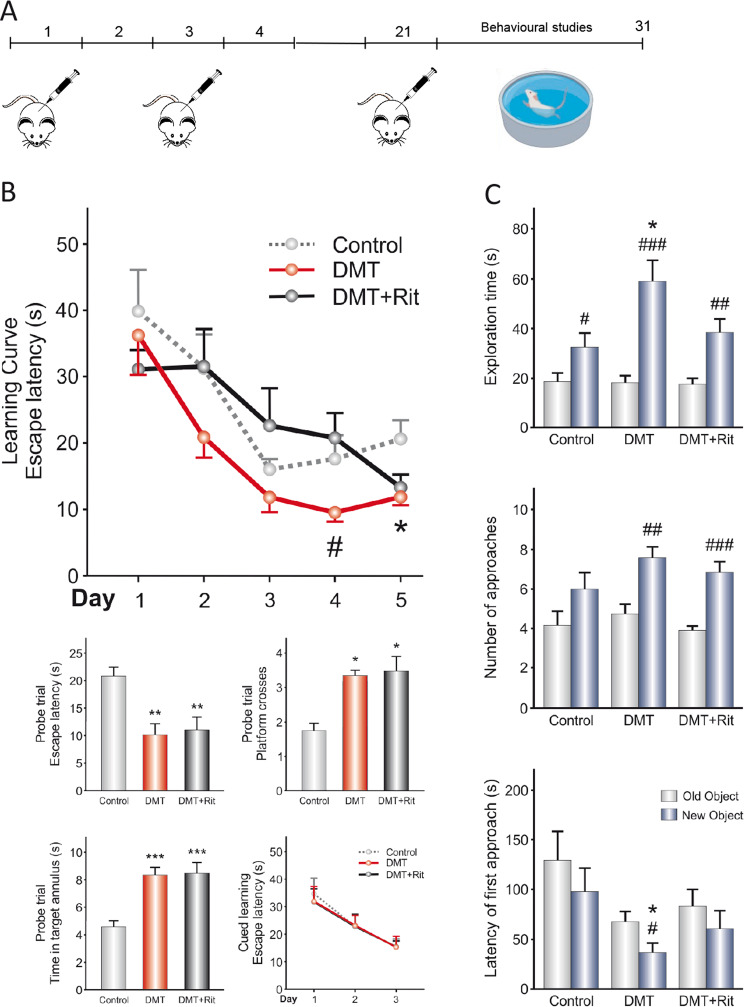
Fig. 5. N,N-dimethyltryptamine (DMT) promotes improved performance in learning tasks linked to hippocampal neurogenesis.
a Schematic representation of the experimental design for behavioral tests. DMT alone or in combination with the antagonist ritanserin (Rit) was intraperitoneally injected on alternating days for 21 days. Then, behavioral tests were performed for 10 days, and finally animals were sacrificed on day 31. b Data from Morris water maze test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 versus the control group. #P < 0.05 versus DMT + ritanserin group. c Data from the novel object recognition test. Values represent the mean ± SEM (n = 12 per group). *P < 0.05 versus the control group. #P < 0.05; ##P < 0.01; ###P < 0.001 versus old object. After confirming the significance of the primary findings using ANOVA, a significance level of P < 0.05 was applied to all remaining post hoc (Tukey test) statistical analyses.