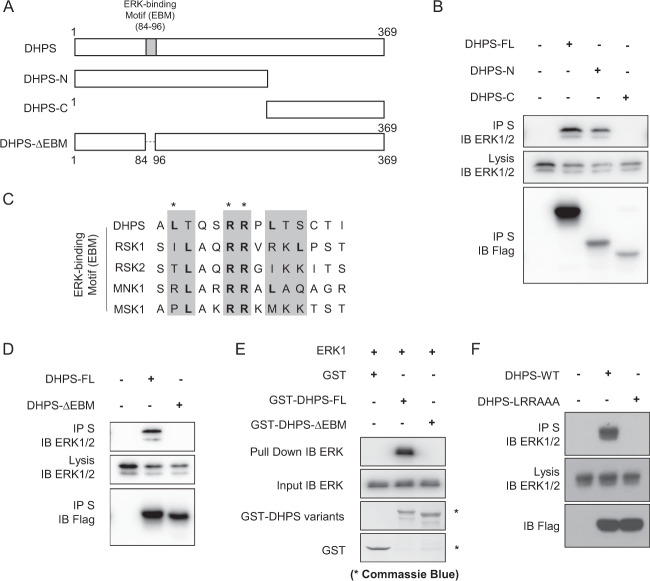
Fig. 2. DHPS Interacts with ERK1/2 through Its EBM.
a Schematic illustration of the DHPS deletion variants used below. b Interaction between the N-terminus of DHPS and ERK1/2. SFB-tagged full length (FL) or N- or C-terminus of DHPS was expressed in HEK293T cells. Cell lysates were pulled down with S protein beads, and the indicated proteins were detected by Western blotting. Data represent a representative experiment from three independent experiments. c Sequence alignment between DHPS and other ERK-binding proteins indicate a possible EBM. The basic residues are marked with asterisks. d Deletion of EBM in DHPS abolishes the binding between DHPS and ERK1/2. SFB-tagged full length (FL) or ∆EBM of DHPS was expressed in HEK293T cells. Cell lysates were pulled down with S protein beads, and the indicated protein was detected by Western blotting. Data represent a representative experiment from three independent experiments. e In vitro interaction between DHPS-FL/∆EBM and ERK. Purified ERK protein was incubated with GST, GST-DHPS-FL protein, or GST-DHPS-∆EBM protein. The pull-down assay was performed with glutathione agarose, and the indicated proteins were detected by Western blotting or Coomassie Blue staining. f Mutations of negatively charged residues in EBM of DHPS abolish the binding between DHPS and ERK1/2. SFB-tagged WT or LRRAAA variant of DHPS were expressed in HEK293T cells. Cell lysates were pulled down with S protein beads, and the indicated proteins were detected by Western blotting. Data represent a representative experiment from three independent experiments.