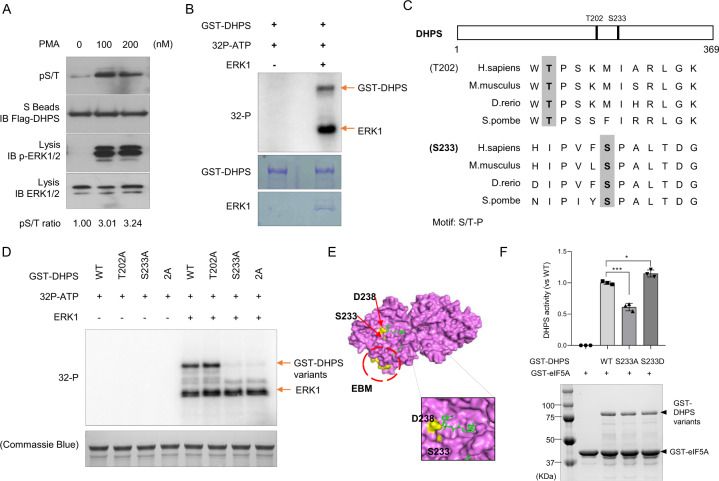
Fig. 3. Identification of Ser-233 in DHPS as an ERK Phosphorylation Site.
a Western blotting of exogenous DHPS phosphorylation in HEK293A cells. HEK293A cells expressing SFB-tagged DHPS were exposed to DMSO or different dosages of PMA for 30 min. Cell lysates were pulled down with S protein beads, and the indicated proteins were detected by Western blotting. Relative levels of pS/T signals after normalization to the flag signals were shown. Data represent a representative experiment from three independent experiments. b In vitro kinase assay of DHPS. Purified GST or GST-DHPS was incubated with or without ERK. γ-32P signals were detected by PhosphorImager. The proteins were detected by Coomassie Blue staining. Arrows mark the radiative signals of GST-DHPS phosphorylation and ERK auto-phosphorylation. c Sequence alignment indicates two possible ERK phosphorylation sites (S/T-P) that are highly conserved from yeast to humans. d In vitro kinase assay of DHPS variants. Purified GST-DHPS-WT or variants (T202A, S233A, 2A/T202A-S233A) were incubated with or without ERK. γ-32P signals were detected by PhosphorImager. The proteins were detected by Coomassie Blue staining. Arrows marked the radiative signals of GST-DHPS phosphorylation and ERK self-phosphorylation. Data represent a representative experiment from three independent experiments. e Surface of the human DHPS-dimer crystal structure (PDB: 1ROZ). The substrates are marked as green (upper: NADPH, lower: spermidine). Ser-233 (S233) is marked with yellow and is located in the NADPH binding pocket. The other essential amino acid, Asp-238 (D238), is also marked with yellow. The EBM described in this study is circled and marked with yellow. A close-up of the surface, including the Ser-233 site, is shown in the right panel. f Comparison of enzymatic activities of DHPS variants. The enzymatic activity assays were performed with purified GST-eIF5A (1 μg proteins in each sample) and different GST-DHPS variants (0.2 μg proteins in each sample). The proteins were detected by Coomassie Blue staining. Arrows mark the proteins of GST-DHPS variants and GST-eIF5A. The activities of the mutant enzymes are expressed as percent of the wild-type enzyme in each group. Results were presented as means ± S.D. from three independent experiments. ***, p < 0.001. *, p < 0.05. P values were obtained using Student’s t test.