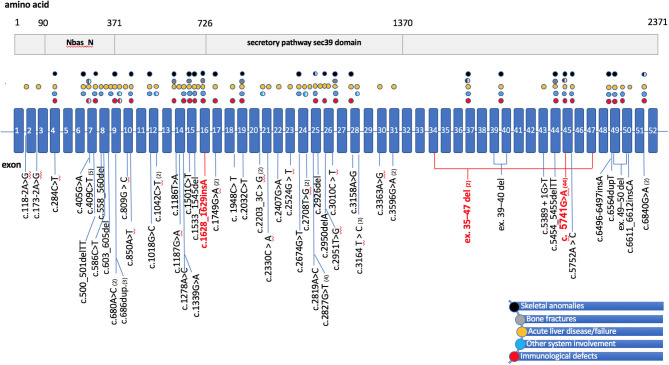
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the NBAS gene/protein with mutations of patients in literature and their main symptoms. (Top) A schematic representation of the NBAS protein, showing the two predicted functional domains: neuroblastoma-amplified sequence, N-terminal (NBAS_N) and secretory pathway protein Sec39 (Sec39). (Bottom) The NBAS gene structure, with exons (numbered 1–52) indicated by boxes and introns by a straight blue line. Positions of mutations are displayed below the gene diagram. Mutations of patients in the current study are highlighted red, mutations reported to date are shown in black, and parentheses include the numbers of cases described. Colored circles above the gene scheme refer to patients' clinical features and correspond to the mutations below the gene diagram, with circles colored as follows: black for skeletal anomalies, including facial dysmorphism, short stature, skeletal dysplasia; gray for bone fractures; yellow for acute liver failure or acute liver disease triggered by fever; blue for involvement of other systems, including Pelger-Huët anomaly and optic nerve atrophy; red for immunodeficiency. Partially filled circles indicate that the clinical features have been detected in only some of the individuals with the particular mutation. del, deletion; dup, duplication; ins, insertion.