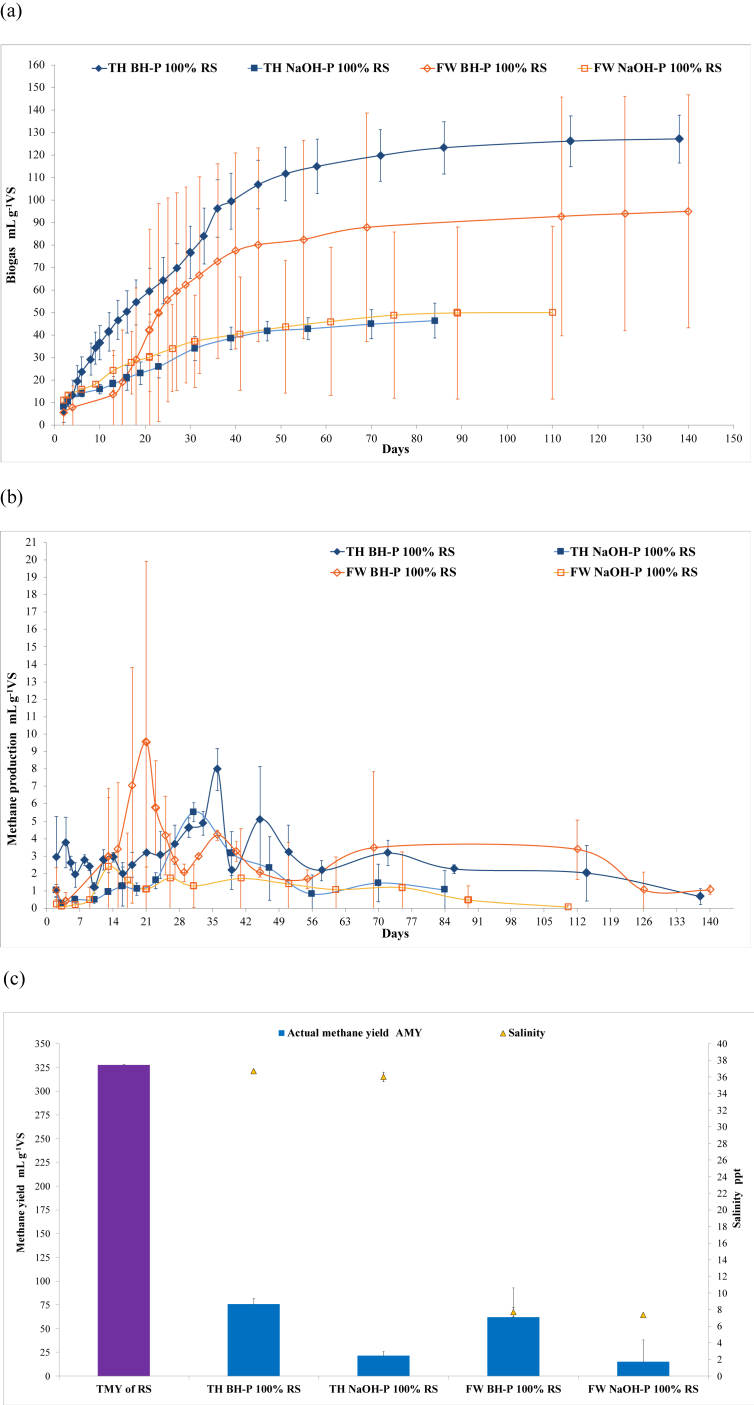
Figure 2.
The anaerobic monodigestion (AMD) of the biological hydrolysis- (BH-P) and NaOH-pretreated (NaOH-P) rice straw (RS) under freshwater (FW) and thalassic (TH) conditions, showing the (a) cumulative biogas production, (b) methane production rate, and (c) AMY (n = 3, error bar = s.d.). The BH-P was performed for 3 days using the hydrolytic bacteria (HB) inoculum that was developed for FW and TH conditions. The NaOH-P was performed for 5 days by adding 3% (w/w) NaOH pellet to feedstock and mixing distilled water and seawater for FW and TH conditions, respectively. The measurement of the (a) cumulative biogas production and (b) methane production rate of the TH BH-P of 100 % U ( ), 75U:25RS (
), 75U:25RS ( ), 50U:50RS (
), 50U:50RS ( ), 25U:75RS (
), 25U:75RS ( ), and 100% RS (
), and 100% RS ( ) was done until biogas production stopped. The (c) AMY (
) was done until biogas production stopped. The (c) AMY (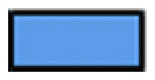 ) of the TH BH-P 100% RS, TH NaOH-P 100% RS, FW BH-P 100% RS, and FW NaOH-P 100% RS was compared to the theoretical methane yield (TMY,
) of the TH BH-P 100% RS, TH NaOH-P 100% RS, FW BH-P 100% RS, and FW NaOH-P 100% RS was compared to the theoretical methane yield (TMY,  ) of RS, while indicating the salinity (
) of RS, while indicating the salinity ( ) of the AMD batch digesters (n = 3, error bar = s.d.). The AMY and TMY were computed using Eqs. (1) and (3), respectively. The results showed that BH-P was better than NaOH-P under both conditions (P = 0.008). However, the AMY of TH BH-P was comparable to FW BH-P (P = 0.182), resulting in the utilisation of TH BH-P in anaerobic co-digestion (ACD).
) of the AMD batch digesters (n = 3, error bar = s.d.). The AMY and TMY were computed using Eqs. (1) and (3), respectively. The results showed that BH-P was better than NaOH-P under both conditions (P = 0.008). However, the AMY of TH BH-P was comparable to FW BH-P (P = 0.182), resulting in the utilisation of TH BH-P in anaerobic co-digestion (ACD).