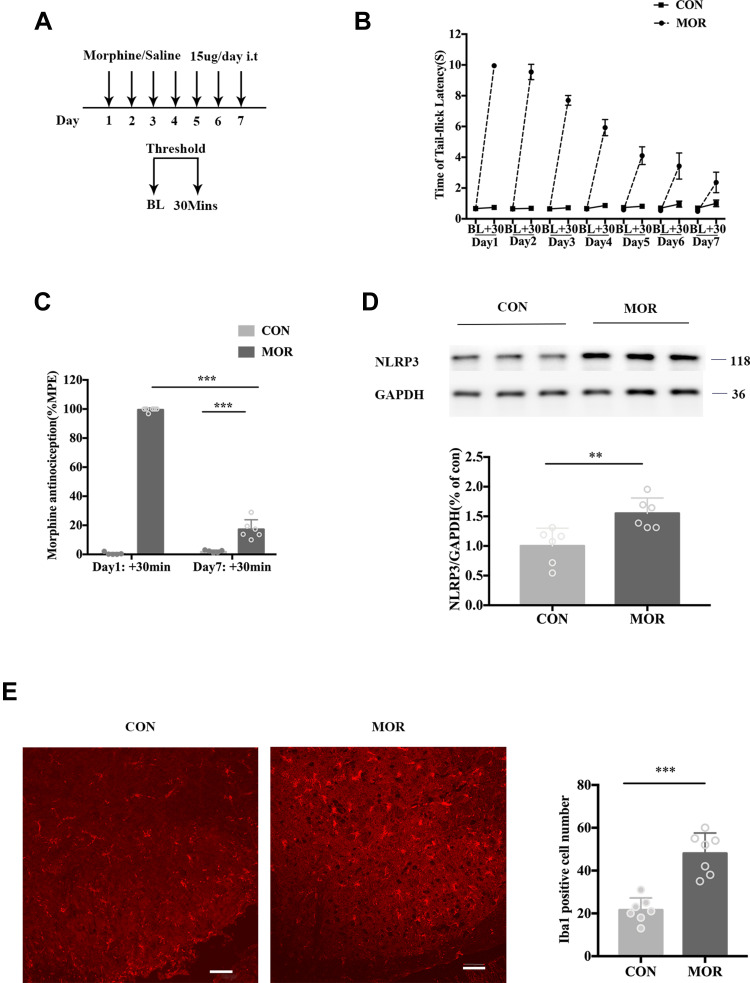
Figure 1.
Repeated morphine treatment induced antinociceptive tolerance accompanied by an upregulation of NLRP3 and the activation of microglia. (A) Schematic representation of the experimental timeline. Mice received morphine (15 μg, i.t.) or normal saline (NS) (15 μL, i.t.) daily for 7 days. On each day, the baseline thermal threshold (BL) before treatment and a threshold of 30 min (+30 min) after treatment were tested by a tail-immersion test. (B) The withdrawal latency in the tail-immersion test before and 30 min after treatment. (C) The %MPE of mice treated with saline (CON) and morphine (MOR) on day 1 and day 7, ***p < 0.001. (D) Expression of NLRP3 of mice treated with saline and morphine. Columns and errors are presented as mean ± SEM. n = 6, **p<0.01. (E) Immunofluorescence of Iba1 (red) in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord of mice treated with saline (CON) and MOR. Scale bar = 50 μm. Columns and errors are presented as mean ± SEM; n = 7, ***p<0.001.