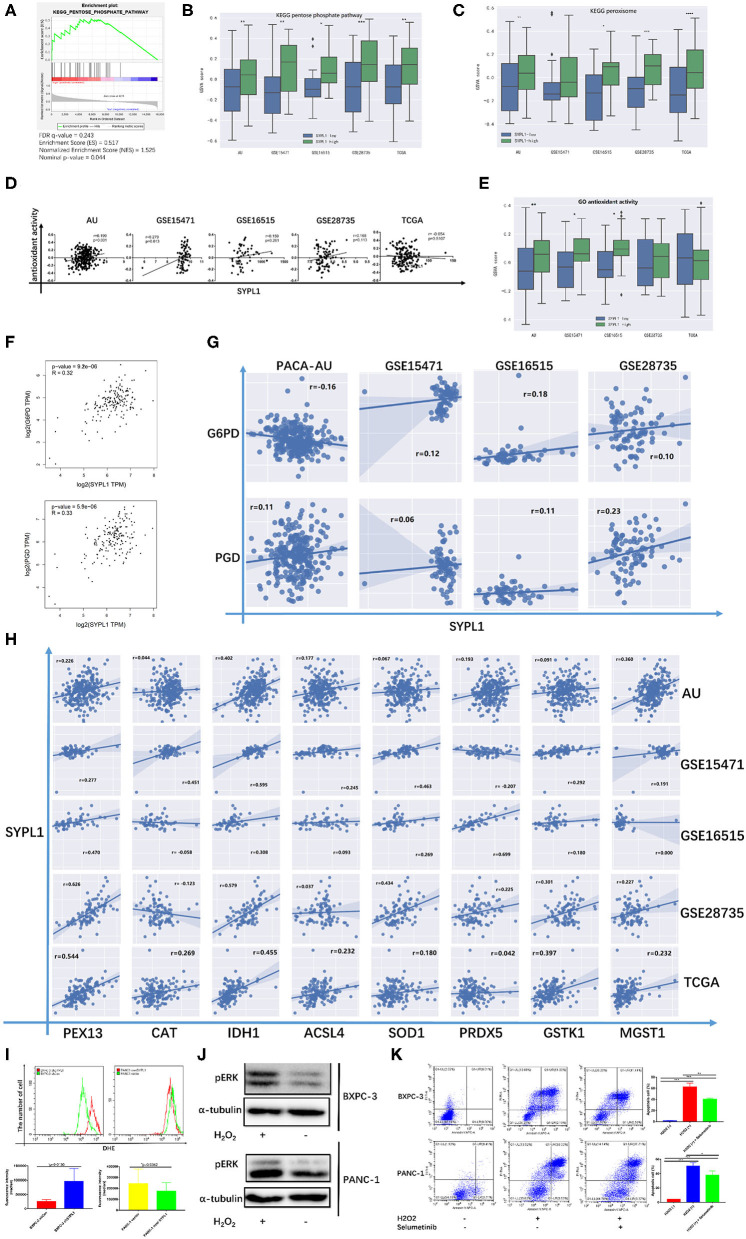
Figure 7.
Knockdown of SYPL1 activated ERK through elevation in ROS. (A) GSEA analysis showed that the expression of SYPL1 was related to the KEGG pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) in the TCGA dataset. (B) The GSVA score of the PPP gene set in SYPL1-high and SYPL1-low samples. (C) The GSVA score of the peroxisome gene set in SYPL1-high and SYPL1-low samples (Both tumor tissues and adjacent tumor tissues of GSE15471, GSE16515, and GSE28735 were taken into analysis in (B,C), while TCGA and PACA-AU included only tumor tissues). (D) The expression of SYPL1 was positively correlated with the GSVA scores of the GO antioxidant activity gene set. (E) The GSVA score of the antioxidant activity gene set in SYPL1-high and SYPL1-low patients (only tumor tissues were included). (F) In GEPIA, the expression of SYPL1 positively correlated with G6PD and PGD, enzymes generating NADPH in PPP. (G) The expression of SYPL1 positively correlated with G6PD and PGD in the other four datasets. (H) The expression of SYPL1 positively correlated with PEX13, CAT, IDH1, ACSL4, SOD1, PRDX5, GSTK1, and MGST1, which were reported to be antioxidants. (I) Flow cytometry showed that knockdown of SYPL1 led to upregulated ROS and vice versa. (J) Hydrogen peroxide upregulated phosphorylated ERK. (K) Hydrogen peroxide led to apoptosis of cells. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 and ****p < 0.0001.