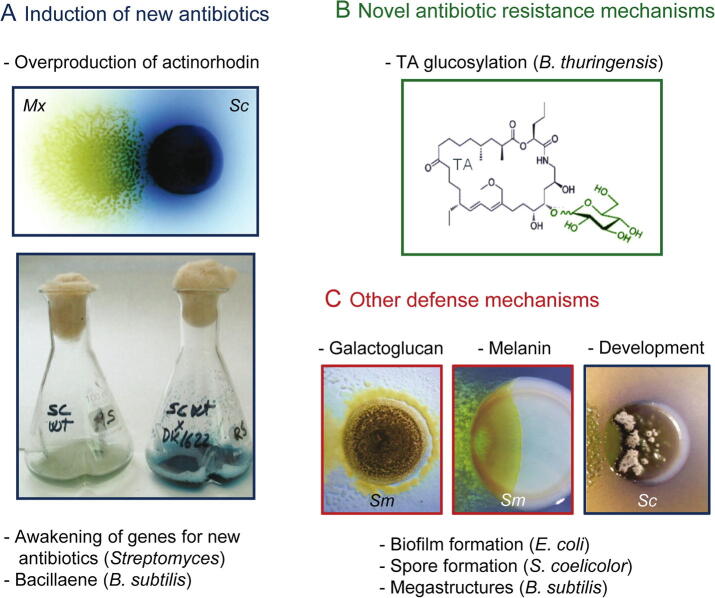
Fig. 3.
Defense mechanisms in the prey with biotechnological applications. A. Silenced antibiotics are induced in the prey during the predatory process. In the pictures, M. xanthus (Mx, predator) induces in Streptomyces coelicolor (Sc, prey) the blue antibiotic actinorhodin, in solid and liquid media. B. Novel antibiotic resistance mechanism have been discovered in B. thuringensis: myxovirescin TA glucosylation. C. Other physical/chemical defenses mechanisms induced by M. xanthus predation in different bacteria. Galactoglucan (left picture) and melanin (middle picture) protect Sinorhizobium meliloti from predation. M. xanthus induces development in Streptomyces (right picture). Pictures from panel A and right picture from panel C are reproduced from Pérez et al. (2011) Microb Biotechnol 4: 175–183. Left picture in panel C is adapted from Muñoz-Dorado et al., (2016) Front Microbiol 7: 781. Middle picture in panel C is from Contreras-Moreno et al. (2020) Front Microbiol 11: 94. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)