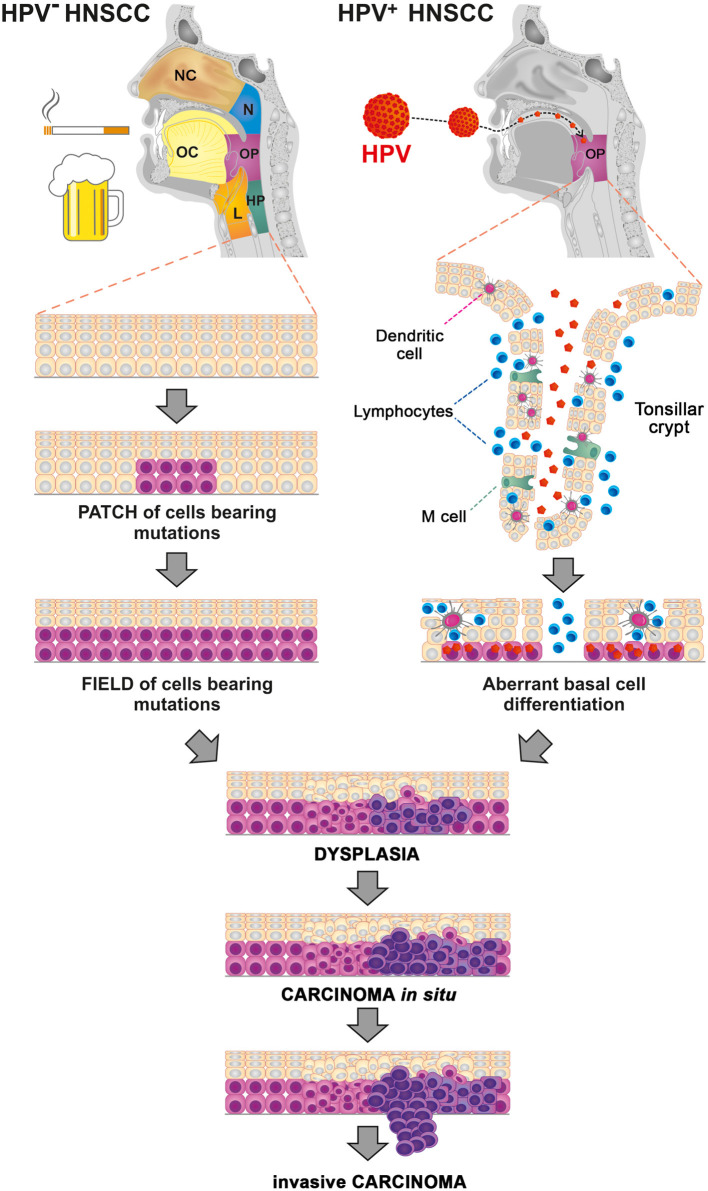
Figure 1.
Processes of carcinogenesis in human papillomavirus (HPV)-negative and HPV-associated head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Tobacco- and alcohol-related mutagens induce widespread mutagenesis in the cells that form the stratified squamous cell epithelium of the upper aerodigestive tract, including the nasal cavity (NC), oral cavity (OC), nasopharynx (N), oropharynx (OP), hypopharynx (HP), and larynx (L). HPV preferentially infects the basal cell layer of the reticulated epithelium of the tonsillar crypts, thus promoting the malignant transformation of epithelial cells within the oropharyngeal region (OP).