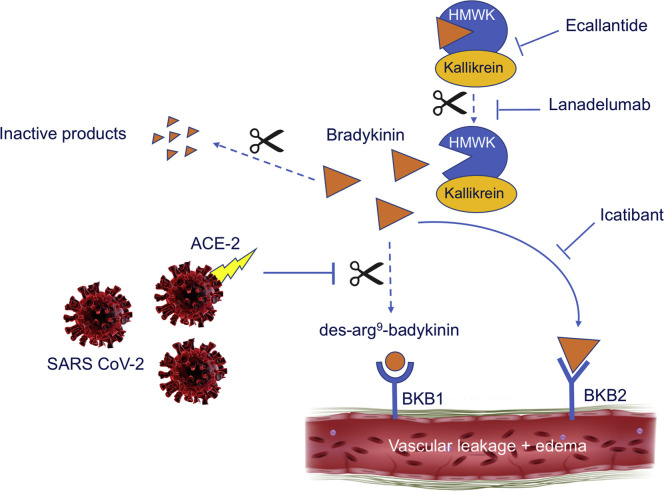
Fig 1.
Proposed mechanism of increased vascular leakage and edema through activation of the BKB1 and BKB2 receptors by bradykinin, and possible therapeutic options. SARS-CoV-2 binds to the ACE-2 receptor. Bradykinin, which is generated when high-molecular-weight kininogen (HMWK) is cleaved from plasma-kallikrein, attaches to the BKB2 receptor, creating vascular leakage. Suppression of ACE-2 will impair the hydrolysis of des-Arg9-bradykinin. Consequently, increased activation of the BKB1 receptor will lead to extra vascular leakage, resulting in pulmonary edema. Ecallantide, lanadelumab, and icatibant all target the bradykinin system and may open new therapeutic options.