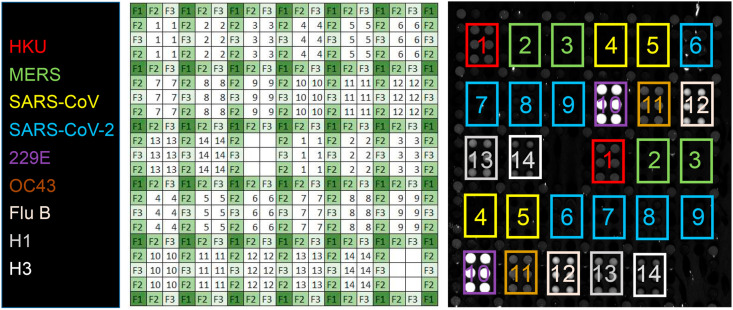
Fig. 1.
AIR assay for antibodies to respiratory viruses. For each antigen, six replicate spots are printed in two different locations on the chip. Each group of six spots is surrounded by negative control reference spots (anti-FITC). Blank (background) areas are included as additional negative controls. Key: 1: human coronavirus (HKU isolate) spike glycoprotein, aa 1–760; 2: MERS-CoV spike glycoprotein, S1 domain; 3: MERS-CoV spike glycoprotein, receptor binding domain (RBD); 4: SARS-CoV spike glycoprotein, S1 domain; 5: SARS-CoV spike glycoprotein, RBD; 6: SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein, S1+S2 ECD; 7: SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein, S2 ECD; 8: SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein, S1 domain; 9: SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein, RBD; 10: human coronavirus (HCoV-229E isolate) spike glycoprotein, S1+S2 ECD; 11: human coronavirus (HCoV-OC43 isolate) spike glycoprotein, S1+S2 ECD; 12: influenza B/Brisbane/2008 hemagglutinin; 13: influenza A/California/2009 (H1N1) hemagglutinin; 14: influenza A/Wisconsin/2005 (H3N2) influenza. F1, F2, and F3 are derived from spotting three different dilutions of anti-FITC. The image at right is a representative array exposed to Pooled Normal Human Serum (PNHS) at a 1:4 dilution.