Figure 3.
CRISPR-Cas9-Mediated Genome Editing of CFAV-EVE1 in Aedes aegypti
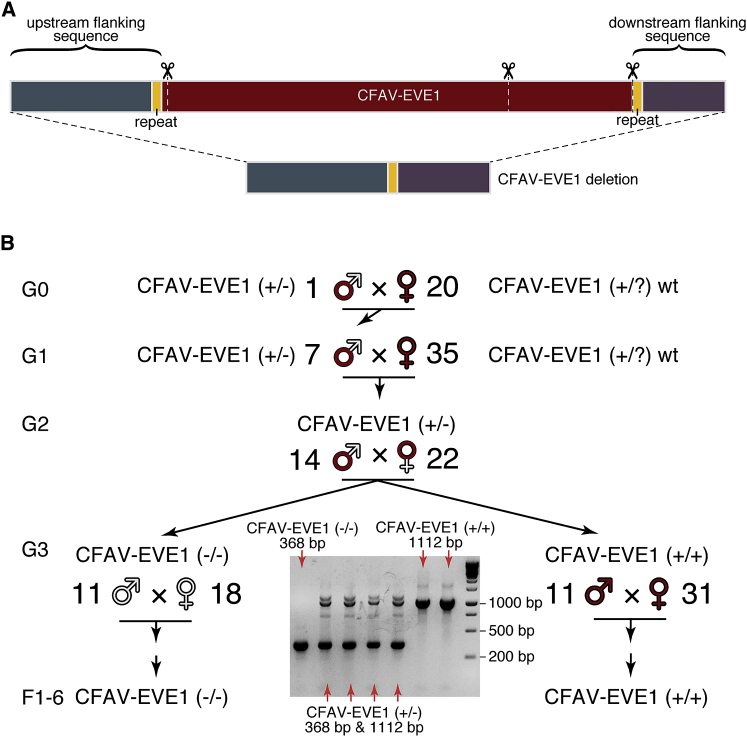
(A) Deletion of the CFAV-EVE1 from the Ae. aegypti genome of the CFAV-free isofemale line using CRISPR-Cas9. The upper bar represents the CFAV-EVE1 with the flanking regions, and the three sgRNA target sites are shown with scissors. The lower bar represents the merged flanking regions without the CFAV-EVE1, where the short repeat sequences in the flanking regions (yellow segments on both bars) are merged into one.
(B) Generation of the CFAV-EVE1 (+/+) and (−/−) Ae. aegypti lines after CRISPR-Cas9-mediated genome editing. A single G0 male mosquito heterozygous for the CFAV-EVE1 deletion (+/−) was outcrossed with wild-type females harboring the CFAV-EVE1. The resulting heterozygous male G1 progeny was outcrossed with wild-type females harboring the CFAV-EVE1. The G2 heterozygotes of both sexes were intercrossed to produce a mixed G3 progeny that was sorted into pure homozygous CFAV-EVE1 (+/+) and (−/−) lines. The letter G denotes the generation of mosquitoes originating from the CFAV-EVE1 heterozygous male and wild-type females. The letter F denotes the generation of the CFAV-EVE1 homozygous lines. The agarose gel picture represents a fraction of samples genotyped at G3, where the pure homozygous individuals were selected by PCR genotyping of a single leg.