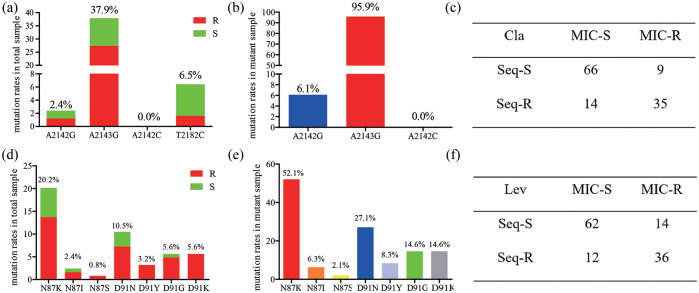
Figure 1.
Profile of clarithromycin- and levofloxacin-related resistance genotypes in biopsies. (a) Prevalence of point mutations in 23S rRNA in total samples; (b) prevalence of point mutations in 23S rRNA in mutant samples; (c) consistency between the 23S rRNA gene sequence and E-test result; (d) prevalence of amino mutations in gyrA in total samples; (e) prevalence of amino mutations in gyrA in mutant samples; (f) consistency between the gyrA gene sequence and E-test results.
Cla, clarithromycin; Lev, levofloxacin; MIC, minimum inhibitory concentration; R, resistant; S, susceptible; Seq-R, sequence result contain a point mutation (A2142G, A2143G, and/or A2142C point mutations for the 23S rRNA gene; point mutations resulting in the amino mutations N87K, N87I, N87S, D91N, D91Y, D91G, and/or D91K for the gyrA gene sequence); Seq-S, sequence result was the same as the reference sequence.