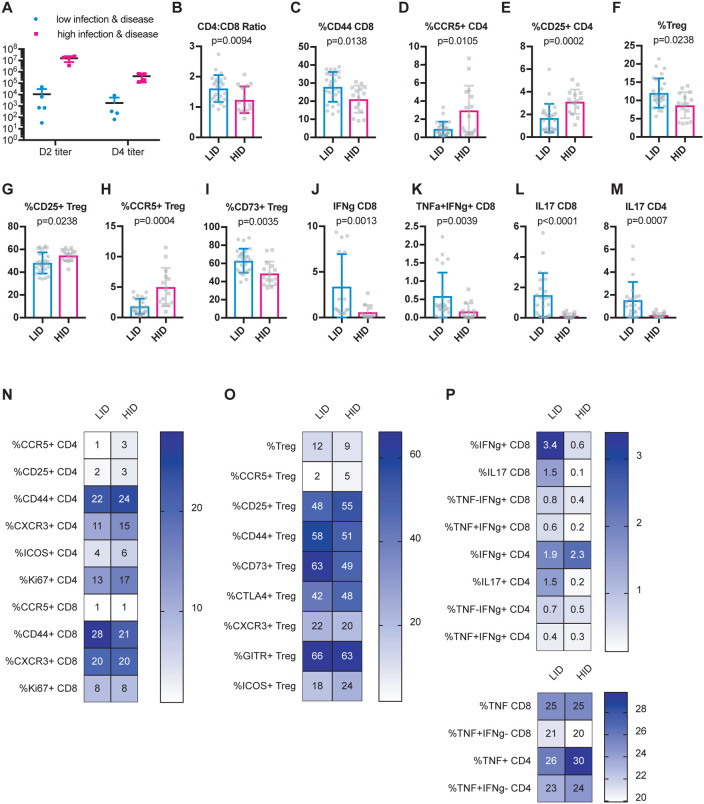
Figure 4. Baseline activated CD8 T cells and Tregs correlate with severe virologic and disease outcomes upon SARS-CoV infection.
Age-matched female CC-RIX were infected intranasally with SARS-CoV MA15 and mice were monitored for death, weight loss, and lung viral loads. To identify possible baseline immune predictors of both viral replication as well as disease upon infection, we classified CC-RIX lines with extreme phenotypes based on both lung viral loads at days 2 and 4 post-infection, as well as weight loss and mortality. Lines were categorized as “low infection and disease” (LID), which had 0–5% weight loss upon infection, no death, day 2 average lung viral titers of <105 and average day 4 lung viral titers of <104 (N=5 lines). Conversely, N=4 lines were categorized as “high infection and disease” (HID) if they experienced greater than 15% weight loss and death, as well as average lung viral titers at day 2 post-infection of >106 and average lung viral titers at day 4 post-infection of >105. Lung viral titers from these 9 CC-RIX lines are shown for days 2 and 4 post-infection (A). Mice from a second cohort of 3–6 age-matched male mice of these selected 9 lines were euthanized and splenic cells analyzed by flow cytometry staining to determine the CD4:CD8 ratio (B), % of CD8 T cells that are CD44+ (C), % of CD4 T cells that are CCR5+ (D), % of CD4 T cells that are CD25+ (E), % of CD4 T cells that are Foxp3+ Treg (F), % of Tregs that are CD25+ (G), % of Tregs that are CCR5+ (H), and % of Tregs that are CD73+ (I). In addition, splenic cells were treated with anti-CD3/CD28 for intracellular cytokine staining assessment of (J) %IFNg+ of CD8 T cells, (K) %TNF+IFNg+ of CD8 T cells, (L) %IL-18+ of CD8 T cells, and (M) %IL-17+ of CD4 T cells. Statistical significance was determined by Mann-Whitney test. (N-P) Heat maps were made to compare the average percent of the indicated cell populations. No statistical significance (p>0.05 by Mann-Whitney test) was found for any comparisons except those indicated in Figures 4B–M.